0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views29 pagesHormonal Regulation
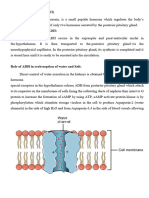
The document discusses hormonal regulation of tubular reabsorption and secretion in the kidneys, focusing on key hormones such as Angiotensin II, Aldosterone, Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP), and Parathyroid Hormone (PTH). It explains the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System's role in response to low blood volume and pressure, as well as the effects of ANP and PTH in regulating sodium and calcium levels. The document also includes a quiz to reinforce understanding of these concepts.
Uploaded by
merilkate1027Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views29 pagesHormonal Regulation
The document discusses hormonal regulation of tubular reabsorption and secretion in the kidneys, focusing on key hormones such as Angiotensin II, Aldosterone, Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP), and Parathyroid Hormone (PTH). It explains the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System's role in response to low blood volume and pressure, as well as the effects of ANP and PTH in regulating sodium and calcium levels. The document also includes a quiz to reinforce understanding of these concepts.
Uploaded by
merilkate1027Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd