0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views36 pagesUnderstanding Neural Networks and ANNs
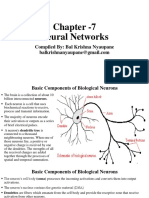
The document explains the functioning of human brains and artificial neural networks (ANNs), highlighting their similarities in processing information. It details the structure of ANNs, including input, hidden, and output layers, and discusses various learning methods such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Additionally, it outlines the advantages of neural networks over conventional techniques and their applications in various fields.
Uploaded by
dhairyasaluja2009Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views36 pagesUnderstanding Neural Networks and ANNs
The document explains the functioning of human brains and artificial neural networks (ANNs), highlighting their similarities in processing information. It details the structure of ANNs, including input, hidden, and output layers, and discusses various learning methods such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Additionally, it outlines the advantages of neural networks over conventional techniques and their applications in various fields.
Uploaded by
dhairyasaluja2009Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd