0% found this document useful (0 votes)
154 views7 pagesUnderstanding Breadboard Types and Uses
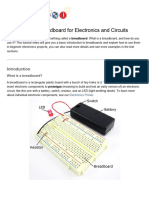
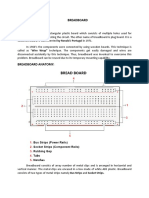
A breadboard is an essential tool for electronic prototyping, allowing users to assemble and test circuits without permanent soldering, making it ideal for experimentation and learning. There are two main types: solderless breadboards for quick testing and solderable protoboards for durable, long-term projects. While breadboards are versatile and cost-effective, they are not suitable for high-voltage applications or complex designs due to potential reliability issues.
Uploaded by
deysayandey21Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
154 views7 pagesUnderstanding Breadboard Types and Uses
A breadboard is an essential tool for electronic prototyping, allowing users to assemble and test circuits without permanent soldering, making it ideal for experimentation and learning. There are two main types: solderless breadboards for quick testing and solderable protoboards for durable, long-term projects. While breadboards are versatile and cost-effective, they are not suitable for high-voltage applications or complex designs due to potential reliability issues.
Uploaded by
deysayandey21Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd