0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views37 pagesBrain Tumor
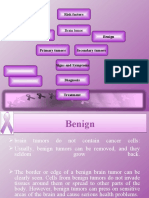
Brain tumors are abnormal cell masses in the brain that can be malignant or benign, causing increased intracranial pressure. The exact cause is unknown, but risk factors include radiation exposure, family history, and certain environmental factors. Treatment involves diagnostic tests, monitoring, surgical removal, and may include radiation and chemotherapy.
Uploaded by
ahmedmagid718Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views37 pagesBrain Tumor
Brain tumors are abnormal cell masses in the brain that can be malignant or benign, causing increased intracranial pressure. The exact cause is unknown, but risk factors include radiation exposure, family history, and certain environmental factors. Treatment involves diagnostic tests, monitoring, surgical removal, and may include radiation and chemotherapy.
Uploaded by
ahmedmagid718Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd