0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views9 pagesChapter 7
The document discusses the chemistry of alcohols, phenols, and ethers, including their definitions, reactions, and properties. It includes various questions and answers related to the identification and classification of these compounds, as well as their reactions with different reagents. Additionally, it covers methods of distinguishing between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, along with specific reactions such as the Kolbe Schmidt and Reimer-Tiemann reactions.
Uploaded by
mrquenicCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views9 pagesChapter 7
The document discusses the chemistry of alcohols, phenols, and ethers, including their definitions, reactions, and properties. It includes various questions and answers related to the identification and classification of these compounds, as well as their reactions with different reagents. Additionally, it covers methods of distinguishing between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, along with specific reactions such as the Kolbe Schmidt and Reimer-Tiemann reactions.
Uploaded by
mrquenicCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024
UNIT-7
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
> Marks =6
I > Ale
introduction :- Alcohol and phenol are the derivative of hydrocarbon, They are formed by os
replacement of hydrogen of aliphatic and ydrocat
pyaar ee ee ee a
Alkane ~+OH~ Alcohol
ArH i Ar-OH
Et bem agus ; Phenol 4,
her :- Bthers are formes the replace! y
ot by rae enett of hydrogen atom of aban By) ‘oxy (RO).
‘Alkane 40H Ether yY
sctit e stions —
1. Which of the compound is Aspirin ~ y
(i) Acetyl salicylic acid (ji)Salicylic acid _(ii)Ae = (iv)Salicyl amide
2, Which is used for poisoning the alcohol- mae y
Methyl alcohol (ii) Ethyl Alcohol (il) Glygerige- (iv) All the above
3, Which is identified by Lucas reagent —
Vay %
(ivAlconol
hd zs
(i) Phenol (ii)Ether —(iii)Aldehyde
4, Carbolic acid is —
@ Phenol) (ii) Phenyl benzoate (i
5, Lucas reagent is i
1804, (ii)ghydrous ZnCle (iv) Cones HCl and anhydrous ZnClz
() Con, HC! (ii) Cone.
6. Which compound is known as ol ofiyinter B21 =
acetate (iv) Salol i
(i) Phenyl benzoate _(i),phenyl saliviate (Gi) pheny!
7, Alcohol react with Na 0. form - 5
(ROR (i) RONa (iii) RL (iv)RCHO
8, Reaction for the formation Of salicylaldehyde from phenol is-
(i) Rosenmund seaction (if) Friedel Crafts reaction (ii) Reimer-Tiem:
(iv) Wurtz’ eaction «
9. Used aganannestietic= |. :
() CHO “(ji CHsOH (iti) CHsCHO (iy) (Calf920
10, Gives Libermann’s nitroso (7 : ne
“ a OH i) CaFls Oe Cte
a densed with -
ann reaction:
i) ¢
20, formed when phenol is cone 5
CHO (i) CHCHO (ii) CotlsCHO (jv) CHCOCHS
Fill in the blanks :- '
i ) formula of alcohol is Cc
faa ether is Call0t20-
2, General formula 0}
BHUPENDRA YADAV ~
62.
99777130098
024
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAIGARH]?
x er used as an ansstbeti:
4 On heating formaldehyde with phenol Bakelite i formed
5 Phenol eats with phthalic acid give acid-base indesor
6 Chlerotoraris formed on heating ethyl sleaba wth bleach
Mai rad of Kote Sci rein of pts
Alcohol is Neutral whereas phenols of aid
9. Ones aol wth cone SO, for 170 alkene oe
10. Edy aleobot ar ethanol i called spPyt of wine. 3 pr
11. Oxidation of pity eleabol gives aldehyde
12. Oxidation of sccondary alcoho gives Ketone.
13, Metyalohol salle
14, Alcohol bare high olin points de to he pesece of hydrogen
1S, Reaction of nitrous acid on a primary amine te form 8
16, Bemzene is formed on heating phenol with Zn powdet.
17, Alcohols are soluble in wate, Its main reason i.
18, Williamson's Synthesis is used inthe manufacture of
19. The dipole moment of ether i less than that of aeobol.
20, Phenol reacts with soumonia to form aniline,
21. Pure alcohol is 100% ethanol
22. Isopropyl benzene is called Cumene.
2. The process of show decomposition of com
fermentation,
24, Anisole reacts with a mixture of
nitro anisole and p-nitro anisole,
25.24,6 Trnitrophenolis called
26, The structure of glycerol is ¢
61
1g powder.
2
a
flex byztite compounds by enzymes is called
enleated 260, and Con, HNO, to give a mixture of o-
@3)
; 4)
th andi IUPAC names propa,
27. The mode of dehydrajG gf alas is 3° alcohol >2°aleohol> alcoho.
8. Formaldehyde rea jenard reagent fo form primary alcohol.
lee :-
‘Answer in one wot
meh Phenol reacts with chloroform and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form
4. Mie esis obtained daring fermentation?
»
‘5. Nami the primary aleohol which gives iodoform
Ethanol (CHs0H) : oe
6, Naine the reaction ia which phenol reacts with chlorofori and sodi
BHUPENDRA YADAV - 9977730098
ium hydroxide(NaOH) to form
6.
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024
salicylaldehyde.
Reimer-Tienann reaction
7 In vitor meyer method, 1 aleobol gives which colour with base
Red
8, Anaesthetic agent is —
her (R-O-R)
Q.1 Differentiate primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol by oxidation and de} dons
method « ay
‘Ans, 1, Oxidation «
aldehydes
rand equal to that
‘CHyCH;OH)__, cH,cHO_!_, cH,CooH
Ethytaleohol "2° Acetaldehyde ‘Acetic acid
Secondary alcohols Secondary aleohels on oxidation eh Shietisiay
selene. Kno onan y egg che ome fain vik
umber or earbon atoms i less than hatin the orig gl
CHy-cH.OB, J,” cH,e=0_ 8 WPesieaox Co, + 20
GY “0? cial inag
Propan-2-0l Acetone: Nagiiewia
‘Tertiary aleohols :- Tertiary alcoholyéré oxigized with difielty as compared to primary and
Secondary alcohols, By the oxidation by strong oxidizing agent (HNOs, KyCr.07) first ketone and
the ai coining leser umber fo om han cool ore
Chis
CHy- C- OH HC = CH, Hl, CH,-C=0 + CO, +H,0
Hy we Roi CH,
‘Tentary butyl aleaho cetone
Tigo} vcscoon al
“ Acetic acid
2, Dehvarogt Sia sen vapour of alcohol is passed over heated Cu at 300 °C. than hydrogen
atom js set jong with the hydrogen atom of OH group, This proces is called
Dehydrogenatons.
18 algoHobon dehydrogenation gives aldehyde,
“yCHCHOH ——, CH,CHO + Hh
“Ethyl alcohol °° Acetaldehyde
2° alcohol on dehydrogenation gives ketone.
CHyCH-OH 2, CHC=0 + Hh
CH (ke Ci
Eu IPENDRA YADAV - 9977730098
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RA
Propan-2-ot Aston aleto give alkenes
4) alcoho are not dl drogennted but lye a water molec #8
ott
Cli,E= CH +120
bee ee
2emethyl prop-1-e
on leohols.
Qa Explain dehydration in primary, secondary and tertiary al :
“has. Denydration = When alcohol is heated with concentrated H,SOs, a moet
fnyrogen atom is released along with the OH group. Other major dy gett RBG #7° HIPOg
P:0s, AhOs, KHSO, and ThO; ete.
Primary alcohol - On heating primary aleohol to high temperat Ryne of dehydrating
agent like con, H,S0, alkene is formed.
CH;CH,OH 7 CH=CH +
Ethanol "2% “Ethene
Secondary and Tertiary aleohols undergo dehydrating shedmmptratvely low temperature,
Secondary alcohol CH;-CH-OH 0? ae 1H, +H;0
CH,
Isopropyl alcohol
Tertiary alcohol CH; Y
ws)” CHs-C=CH, +10
& Hee
Teatiary Butyl al
‘The sequence of dehydratifn of different alcohols is as follows.
3° alcobdh AQ? pleohol > 1° alcohol
9-8 Explain the toes of debydration of aeoho. 09)
fm. Deir irati : a ae is heal with concentrated H,SO, , a molecule of water is
iol to form an alkene, This reaction is call tio i
Behy ahi: j8 released along with the OH group, ee
CH;CH,OH _l
Bet
released fom te alcohol to form an alkene, This reaction is called dehy draeQee™ In this a
(CH= CH + 1,0
Med or penvération Nesta 7
ie a \ehydration :- Mechsnism of dehydration of alcohol involves the following steps~
tion of protonated alcohol (Oxonium salt) ~ One mole of aleoh
‘rotoh to form oxonium salt. This step is reversible, ae
Fast iH
CH;—CH,-O-H +Ht === CH,-cH,-0-H
Protonated dleoho! (Oxonium aleoho!)
BHUPENDRA YADAV -9977730098 65,
Gi) Formation of Carbocation
mainly dehydrating. Ttinvolves
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024
slo which ithe ate determining step and this step is
of water and formation of carbocation.
H +
CH= CH;-O-H ep CH=CH + 10
é carbocation
Gp Formation of Ethene ='This carbocation ely eliminates proton by HSO, by which el
Q.4 What is Lucas reagent ? How are primary, secondary and tert SBF by
it Explain. CO (3,1)
‘Ans, Lueas reagent :- Lucas reagent isa solution of anhydrous Z,
solution is used to classify alcohols of low molecular weight.
(On adding the alcohol to Lucas reagent, a tertiary alcohol re
presipitat(PP1) of alkyl chloride, IF the precipitate appears
Secondary, [fno precipitate is obtained in cold, the alogitisp
‘Tertiary aleohol
CH eS oe)
CHy-C-OH)+ Cons HCI)“ NCCI + HO
Ci CH
(Immediately vy
Secondary alcohol
CHy-CH-OH + com HCR #820 CHy-CH-Cl + HO
chy CH
(after five mit
Primary alcohol
CHy-CHr-OBS Meo Hicl “YS 20, No reaction
(No turbidity s produced)
Q5-Write Vj PSS
units
Ans. Vie feys? method : The test completed in the following steps-
(i The elvelfgloohol is first converted tothe alkyl iodide by reaction with concentrated HI.
is treated with silver nitrite (AgNO;) to form nitroalkane.
ei finally treated with nitrous acid (HONO) and made alkaline with NaOH,
—+ Jfa blood red colour is obtained, the original alcohol is primary.
—+'If' blue colour is obtained, the alcohol is secondary.
—+ If no colour is produced, the alecko is tertiary,
CH=CH, +HSO, ep CH= CH, + H,S0,
Ethene
‘This way, acd used in the firs step () i released instep (Il).
‘method to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol,
Primary alcohol
BHUPENDRA YADAV -9977730098 66.
See
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024
3, __| Litmus test Turn blue litmus red. Does not affect litmus paper
4, _ | Ferric chloride ‘On treating with neutral FeCl; ‘Alcohol does not give any .
test solution phenol gives red to
violet colour. ve ee
3, | Reaction with ‘No reaction. Ethyl hailde is obtained.
halogen acids : ral
6. Bromine water | Phenol gives light yellow Alcohol does not ‘omipe
test precipitate of its bromo water test.
derivative.
7, |Todoformtest | Phenol docs not give idoform | It gives ae form yellow
test. ppt) \
Q.8 Compare Ethyl aleohol and Diethyl ether. QR
4
Ans.
SINo. Test Ethylaleohol__g \_ Diethyl ether
1 | Physical test Volatile liquid high BP. Geos] Volatile liquid low B.P. due
H-bond. to absence of H-bond.
No reaction
2 | Reaction with Hydrogen gas is fo)
sodium
3 | Reaction with PCI; | Ethyl chlorid Ethyl chloride is formed when
reacts with Cold POIs, itreacts with PCls on heating. |
7 __|Reaction with air_| No reaction, Forms peroxide.
5___ [Solubility in water_| Soluble inyvater. Immiscible in water.
Q. 9 Explain the following reactions: y
i) Kolbe Schmidt reaction (09) \iipReimer-Tiemann reaction (09,16,17,24)
(iil) Coupling reaction (09,24)
Ans, (i) Kolbe Schmidt régcfion :- When sodium salt of a phenol is heated with CO at 130°C. and
4-7 atm pressure, $0 is formed. his on acidification gives salicylic acid, This reaction
is called Kolbe Schmidt reaction,
Nan & OH oH
O bre oo si oO coon
wo E> ae
cA
Sodium salicylate Salicylic acid or o-hydroxy benzoic acid
(i) ReimerJTi es reaction :- When phenol is treated with chloroform and aqueous sodium
( 0 C, o-hydroxy benzaldehyde and p-hydroxy benzaldehyde are formed. The
orthojsémer is the major product. This reaction is called Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
OH OH
CHO
+ CHCI, + 3NaOH ——> + 3NaCl + 21,0
phénol chloroform o-hydroxy benzaldehyde or Salicylaldehyde
BHUPENDRA YADAV — 9977730098 68.
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 7024
iene pr
nl sweated with zoom chloe inde presence of
Wiping retold Coin
@:xOyoH + Hel
prhydroxyazobenzene
(Gi) Coupling reaction
‘-hydroxyazobenzene are
©xa+ Opou
phenol
Benzene diazonium
chloride
(Q-4WEletrophilic Substitution Reaction (ESR)
"Wie the equation of following reactions of Phenol. ‘
(@Hslogenation — ()Nitation (Gi) Sulphonation _ (jv) Allylajon\\ ¥a}Acylation
(Gi) React with Zn dust (vil) React with Ammonia (vii) React witht anby ride
How cin you obtsined following compounds trom pheio:
(.24.6-Tribromophenol (i) 2,46-Tenitrophenol Pirie acid
(ii) o-bydroxybenzene sulphonic (iv) o¥fesol, p-cresol
(w) echydroxy acetophenone, p-bydroxy aoetophenone (i) Benzene
i il) Phenolphthalene
(vi) Aniline
Ans-(i) Halogenation :- Phenol is react with broming.
bromophenol and p-bromophenol,
OH 0
orAVO .
ih hy Br
OH
‘p-bromophenol
sence of CS; ot CHC! to from o-
2HBr
3
+ 28, ——+ <
Phenols orbs o
2,46-Tribromophenol Phenols is e. bromine water to from white presptate of 2,46-
feel
H
<> "oO
£5 TT «ine
OH
+ 10
"Br 24,6-trbromophenol
ct with dilute nitric acid (FINOS) at low temperature to form o-
Cee ones
mage, ¢
(ii) Nitration ;- Phi
21,0
‘oN ophenol NO, .
. ne pet ophenol
2,4,6-Tyinitrophenol (Picric acid) ; Pheaol is reacts with concentrated HNO, and Concentrated
H,S0j solution to form 2,4,6 Trinitrophenol or picrie acid,
OH OH
oO NO: yy NO;
+ HINO; iso, + 3140
NO: 2,4,6 Trinitrophenol or por
BHUPENDRA YADAV - 997730098 6,
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024
sybenzene sulphonic acid
iy Swhohonaton Phenol is reaet with one $0, form o-ydrox
i Sydroxybenzenc sulphonic acid
OH OH OH
SO
+ HSOEe +
“Iho SOs
‘o-hydroxybenzene _priydroxybenzene
CChlorobenzene
sulphonic acid sulphonic acid
(jv) Alktation + AS
-cresol, p-eresol :- Phenol react with methyl chloride in the presence gia Hy toe
‘o-eresol and p-eresol are obtained.
a oe 3G Na
best amu Oy
+ CHCl anhydrous Al + +
CH
o-ctesol ie
(eta yson, pony acetopenmne
Cp aalar acetophenone, p-bydroxyactopheno
Phehol react with acetyl chloride inthe presence of +e ICI, to ftom o-hydroxy
reatphenone and phony acelophenone
oH Ae) (oH
Gin naan QP? Qo,
sexy loi & . piygiony
* yphenone ‘acetophenone
vi) React wth Za dust = ve
ee cas ‘powder to form Benzene,
anhydrous ZnCl at high temperatare
ted with ammonia inthe presence of
fromtie primary amine( Aniline).
OH 6
+ Nth aiysou ch, O) + 120
~ 9 Kailine
ii React with Phthalic anhydride 5 pt
Ce pthaene: Two molecule of Phono react wih pts anhytrid in he presen ae
ESO, om phenolpilen. which an fr sid base indesor and is used as.
medicine é
BHUPENDRA YADAV - 9977730098
2024
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH
oH
oH
gu gH
0}
g g Con. HSQ¢ 9 q
+
Q ~H0
i as
° Qo»
§ ¢
6 8 phenolpthaein Oo
.Q/11 Give chemical equation of the folowing conversion.
() Ethylene from ethanol (ethyl alcohol.
Diethyl ether from ethanol(ethy! alcohol),
Ethanol(thylaleohol) from diethylether,
(jv) Etly] acetate from ethanol(ethyl alcohol), {
(
(») Ethanol(cthyl alcohol) from glucose,
ss (0 Ethylene from ethanol ethyl alcoho) :-Etyhgled Myon heating a 170°C with
concentrated H:S0,, onc molecule of water is rel alcohol and ethylene is formed
CHCH-OH HO, CH= CH NEED)
at Ethanol = TB
{0 eth eer from ethanol (thy sleahot) \Ophcatng ey aleotol in excess wih
“onesninte’H:SOe one molecule of HO Rata aad dey ther is formed,
GHsOH +1480, WA WHF Hs0, + 1,0
4 ES GHETSO, + Hy
CHS HSO, + Cation AES GHin0.CHt + 1450,
. ethyl ether =
(ii) Ethanol(ethyl alcohol) from are eth When ether is heated with dilute H,$O, in the
Presence of press, th isn esha
ZHs-0-CHae EO jabltiso, 2C41, OH
dit tg So Ken
(Ey ace rete ath is tated with act
5 cohol): When ety! sleohol is treated with
thepesins o LST a Ss ee a
Gee OOH so, Ciscoe sito
Ethyl acetate
BHUPENDRA YADAV ~ 57773009
n,
SCIENCE ACADEMy BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024
Deller Prepared inthe ly
erfication PrOCCSS by the heating 4 .
setts ms y the heating ethy| alcohol ‘ith concentrated sulphuric acid at 140 °C. The
real
ratory and, ‘industry by the Williamson continuous
provceds in Wo stege
Gl we
HIOH + uhiso, — TL. caso, + 0
[HS0, + Fy
convert an exces of alohol into ether. So, this method w elon Williamson conti
iyiatet
CHHIESONS Hoos, wee, Cth.0 cs + Hs0
a a iethy] ether
suiphuric acid is regenerated in the reaction hence, it appears that only a small ay
(@) Water formed in the Teaction dilutes the acid and its reactivity
(B)_Apart of sulphutio acids reduced by alcoho into sulphur dg
1 Deserbe the laboratory method of preparation of det! ty er thus obtained is
prified ? (01,03,05,06,09,10)
fins. Laboratory method of pre
i tion of Diethyl ether | ether is prepared in the
inportory and industry by the Williamson continuous etheretion process bythe heating ey
ol wth concentrated sulphur ald at140
aaa CaulOH HSO, ie Tho
eds in two steps,
ethyl aleohol
CH;[HSO, + HOCH,
rocedur®.- Sehsitol (2 volumes) and concentrated sulphuric acid (1 volume) are taken ina
Enis iye aed afta 413 K, Ethanol is added at the same rate at which ether
7 is collected in arecei in ice-cold water,
digit jad is collected in a receiver cooled in oe-co ee
Puri : Ether contain ethanol, water and sulphuric acid as impuri
Srp nip a ees agitated with 50% solution of calcium chloride o remove alcohol,
ae , 9 a
tis then washed with water, dried over anhydrous calcium chloride and redistilled,
Q.14Pure phenol is a colourless solid but why it is converted into pink after some tim
~ 011,18),
BHUPENDRA YADAY ~9977730098
a
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH | 2024 SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH [2024
2CH,OH + 2Na—_,.
-xplain with react
‘Or What change in colour is observed in phenol in presence of oxygen? Exp kr
‘Ans, When phenol is lef pen in air and ligt, it slowly gets oxized and tus pink. At fis
‘quiaooe is forme which gives an addition reaston with phenol to form a deep pink colour
Substance, which is called phenoguinone
°
ox 6
eo en) eee
© Serene
In pheaoguinoas, two molecules of phenol are linked with one molecule tain a
anaes et
ty pote ~
20. on @ow a @y
Pacoquinaae at coer)
3 esata at et
=
@) What is the reaction of diethyl ether wis
2C4HLONa + 1,
(16 How are the following com
GQ Propene -—» Propandta
(i) Benzyl chloride —, Benzyl alcohol oF
(i) Etylmagnesium chloride ——© Propan-t-ol oy
(is) Mebiyl magnesium bromides 3 methylpropan--a
Ans. () CH;CH= CH, + Con.H,S0, —» + mo +. “ACY 80,
axe mony NS :
* Qnton =. 0" 35,48
versions carried ont:
Benzyl elloride Benzyl aleohol
(Gi) Alkyl halide reacts with sodium alkoxide, (i) CHLCHMECI + HERO one, CHC oe
Gv) Phenol heated with Zn powder. (23)
(9) Ethyl aleobol is treated with B;S0, at 4 (a3) Ethyimagnesium chloride LOH+ Me(OE)C.
- (i reaction ofpheaol with sodiam. | ( ae
‘Ans. (2) Pheals are prepared by hydroly jum salts by water, dl. Acids ets, & ol b b
NCI a (iv) CH)MgBr + CH;-C-O —+ GJ ok 4. HO ——> sae
, ‘Methyl magnesium ‘2-methylpropan-2-01
ee acenia Vere
ane
(i) The reaction of Difthyl elief with conc. HI acid, on heating gives one molecule of ethyl iodide
cohol.
FH __ 100% © GiHpOH + CH
sci and lsh bag aeeet? (115) ee
Oral phen th contin “OH grou, What the reson that pena aie
re?
Maer acids as compared to alcohols is that phenols cxistas a resonance hybrid.
samen bh LE [B
©
Pa
6
©.
&
rome &
QUT Ethyl alcohol and; re contain -OH group. What is the reason that phenol is
Ethanol Ethyl iod ge thy oxygen atom gets a postive charge and attracts the electron pair ofthe O-H_
by reacting ally halide wit sodium alkoxide, fides the release ofa proton. The phenoxide fon formed after the release ofa
fe0CH——* —CHOCH; + NaCl lied by resonance.
CqHOH == CiHO" + HT
« cs obtsined by heating phenol with Za powder Phenoxid on
OH + Zn——> Clg + Zn0 od to the oxygen that’s
11 Seofols, no resonance is possible hence the hydrogen atom is strong!
why Phenol i acidic and sleoho s neutral
(0) Ethers obtained by testing ethyl alcohol with 1,0, et 413 K. i
CREE CHO GH OCH HHO: Q. 18 Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol. Compare its acidity with that
of ethanol.
‘Ans, The reaction showing acidic character of phenol are ~
(vi) Phenol reacts with sodium, sodium phenoxie is formed and hydrogen gas is liberated.
BHUPENDRA YADAV -9977730098 1,
F BHUPENDRA YADAV ~9977730098, B.
f intremeremere sx »
SCIENCE ACADEMY BIAORA, RAJGARH|2024
‘Reaction with sodium - Phenol reacts with sodium to give Hs BAS.
OH
(©) Reaction with NaOH ~ Phenol disolve in NaOH to give sodium phenoxide
OH Na
sodium phenoxide
‘han ethanol, This is duc to the phenoxide fon let fein
‘fom phcnal is subiizedby resonance while eho eleanor
Q.19 Writea notes on fermentation,
‘Ans.The process of slow decompos
SPinbounds in the presence of enzyme eatalyst is called fe
living substance. The enzymes present i
invertase ete,
‘When yea is mixed in glucose solution and kept
result of fermentation,
CHO, ase, 20
i point than that of hydrocarbon, but
© She molecular masses, but:
Point besause propanol in polar
fs presen eto wih a
‘Donding between its molecules: Nene ‘hydrogen bonding is n¢
ofthe polar OH pou
your
as Js Ng Mtl ot polar in sae, When nol dod inweter,
ena mht breaking thong eyeing tae ee
Boye ine
RDB Ornadlo,,
1
Hest Higa h
On te ote hand, bydroctbons are non pole
roleules and be
BHUPENDRA YADAY —9977730098
ox 6 +140 iS)
Pezala mor sid ofa photon
tame?
propanol has a higher boiling
ong inermolecolae hydrogen
ot present due tothe absence
You might also like
- Previous HSE Questions and Answers For The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"No ratings yetPrevious HSE Questions and Answers For The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"10 pages
- Hsslive-Xii-Chem-7. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Qns & AnsNo ratings yetHsslive-Xii-Chem-7. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Qns & Ans15 pages
- CBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDF100% (1)CBSE Class 12 Chem Notes Question Bank Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDF19 pages
- Chapter-09 - Answer Key & Explanation - CHEMISTRY Explanation Alcohol Phenol and EatherNo ratings yetChapter-09 - Answer Key & Explanation - CHEMISTRY Explanation Alcohol Phenol and Eather11 pages
- Alcohols: Structure, Nomenclature, and ReactionsNo ratings yetAlcohols: Structure, Nomenclature, and Reactions34 pages
- 27 Alcohol Phenol Ether Formula Sheets Getmarks AppNo ratings yet27 Alcohol Phenol Ether Formula Sheets Getmarks App15 pages
- NEET Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols & EthersNo ratings yetNEET Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers12 pages
- CLS ENG 22 23 XII Che Target 4 Level 1 Chapter 12No ratings yetCLS ENG 22 23 XII Che Target 4 Level 1 Chapter 1236 pages
- Alcohol Phenol and Ether 26-Sep-2024 16-03-26No ratings yetAlcohol Phenol and Ether 26-Sep-2024 16-03-2634 pages
- Practice Questions On Alcohols and PhenolsNo ratings yetPractice Questions On Alcohols and Phenols11 pages
- 3) 1 - Alcohols - Theory 1 (50-59) FinalNo ratings yet3) 1 - Alcohols - Theory 1 (50-59) Final10 pages
- Alcohols: Types, Preparation, and PropertiesNo ratings yetAlcohols: Types, Preparation, and Properties18 pages
- Alcohols and Phenols: Types and ReactionsNo ratings yetAlcohols and Phenols: Types and Reactions22 pages
- Classification: Alcohols, Phenols and EthersNo ratings yetClassification: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers9 pages
- Che SR Ape M 03 Prep of Alc (11 Jul 2016)No ratings yetChe SR Ape M 03 Prep of Alc (11 Jul 2016)44 pages
- Alcohol Phenol and Ether Practice SheetNo ratings yetAlcohol Phenol and Ether Practice Sheet10 pages
- Alcohols: Structure, Properties, and ReactionsNo ratings yetAlcohols: Structure, Properties, and Reactions11 pages
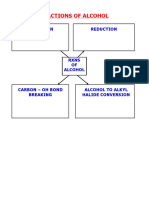
- Reactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductionNo ratings yetReactions of Alcohol: Oxidation Reduction18 pages
- Alcohol, Phenol & Ether Reactions GuideNo ratings yetAlcohol, Phenol & Ether Reactions Guide62 pages
- Hsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-11. Alcohols, Phenols and EthersNo ratings yetHsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers4 pages
- Products and Mechanisms of Alcohol ReactionsNo ratings yetProducts and Mechanisms of Alcohol Reactions6 pages