0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views1 pageMachine Learning: Backpropagation and Gradient Descent: Objective
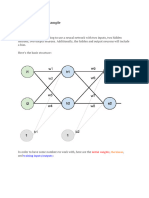
The document explains the training of neural networks using backpropagation and gradient descent. It outlines the forward pass for output generation, the backward pass for error propagation, and the weight updates through gradient descent. The training process involves multiple iterations to minimize the loss function and achieve a trained model.
Uploaded by
epixtunnedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views1 pageMachine Learning: Backpropagation and Gradient Descent: Objective
The document explains the training of neural networks using backpropagation and gradient descent. It outlines the forward pass for output generation, the backward pass for error propagation, and the weight updates through gradient descent. The training process involves multiple iterations to minimize the loss function and achieve a trained model.
Uploaded by
epixtunnedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd