0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views21 pagesOrganizational Control Techniques
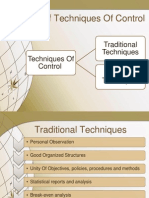
The document outlines various control techniques essential for effective organizational management, categorized into general, special, and advanced techniques. Key methods include personal observation, written communication, budgeting control, quality control, and management information systems, among others. Each technique serves to enhance performance measurement, ensure quality, and facilitate decision-making within the organization.
Uploaded by
Michael AugustinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views21 pagesOrganizational Control Techniques
The document outlines various control techniques essential for effective organizational management, categorized into general, special, and advanced techniques. Key methods include personal observation, written communication, budgeting control, quality control, and management information systems, among others. Each technique serves to enhance performance measurement, ensure quality, and facilitate decision-making within the organization.
Uploaded by
Michael AugustinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd