0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views4 pagesDisclosure Notes
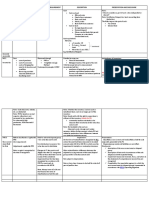
The document outlines the disclosure requirements for inventory and intangible assets in financial statements according to IAS 2 and IAS 38. Key inventory disclosures include accounting policies, inventory categories, carrying amounts, write-downs, and any inventory pledged as collateral. For intangible assets, disclosures must cover accounting policies, carrying amounts, movements, amortization, and impairment losses.
Uploaded by
saniabansal2006Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views4 pagesDisclosure Notes
The document outlines the disclosure requirements for inventory and intangible assets in financial statements according to IAS 2 and IAS 38. Key inventory disclosures include accounting policies, inventory categories, carrying amounts, write-downs, and any inventory pledged as collateral. For intangible assets, disclosures must cover accounting policies, carrying amounts, movements, amortization, and impairment losses.
Uploaded by
saniabansal2006Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd