0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views8 pagesMidterm
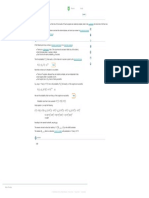
The document outlines various statistical analyses including hypothesis formulation, paired samples t-tests, and the Kruskal-Wallis test to compare different datasets. It concludes that there are no significant differences in readings between Scale A and Scale B, R&D expenses from 2000 to 2001, salary increases among manufacturing plants, and student performance across subjects. Additionally, it identifies Ford as having higher repair costs than Chevy and highlights the most consistent students in academic performance.
Uploaded by
Karen PlazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views8 pagesMidterm
The document outlines various statistical analyses including hypothesis formulation, paired samples t-tests, and the Kruskal-Wallis test to compare different datasets. It concludes that there are no significant differences in readings between Scale A and Scale B, R&D expenses from 2000 to 2001, salary increases among manufacturing plants, and student performance across subjects. Additionally, it identifies Ford as having higher repair costs than Chevy and highlights the most consistent students in academic performance.
Uploaded by
Karen PlazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd