0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views18 pagesName: John Joseph Course: CSC 202 Course Title: Comp Programming Ii MATRIC NO: U23MTH1020 Department: Mathematics
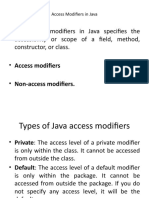
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, detailing its history, characteristics, and classification within programming language generations. It highlights C's features, such as its procedural nature, efficiency, and portability, while also discussing its syntax, data types, and control structures like loops. The conclusion emphasizes C's foundational role in programming and its influence on modern languages.
Uploaded by
johnseleb3Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
63 views18 pagesName: John Joseph Course: CSC 202 Course Title: Comp Programming Ii MATRIC NO: U23MTH1020 Department: Mathematics
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, detailing its history, characteristics, and classification within programming language generations. It highlights C's features, such as its procedural nature, efficiency, and portability, while also discussing its syntax, data types, and control structures like loops. The conclusion emphasizes C's foundational role in programming and its influence on modern languages.
Uploaded by
johnseleb3Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd