0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesHomework 12 Answer
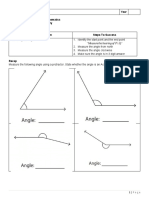
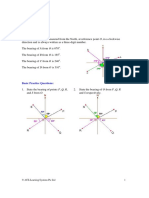
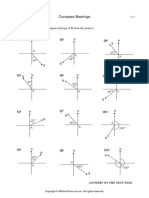
The homework focuses on gradient and bearings, involving calculations of true bearings and distances between various points. It includes problems related to compass bearings, trigonometric functions, and the movement of individuals in different directions. Key tasks include finding bearings, distances, and determining the necessary speed for one individual to meet another.
Uploaded by
htwongCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesHomework 12 Answer
The homework focuses on gradient and bearings, involving calculations of true bearings and distances between various points. It includes problems related to compass bearings, trigonometric functions, and the movement of individuals in different directions. Key tasks include finding bearings, distances, and determining the necessary speed for one individual to meet another.
Uploaded by
htwongCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd