0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views10 pagesOral Lessons Manuscript
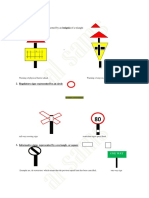
The document is a handbook on traffic signals and driving regulations in Zimbabwe, detailing various types of traffic signs, their meanings, and the rules associated with them. It also outlines the requirements for different vehicle licenses, including age limits and maximum speed limits for various vehicle classes. Additionally, it provides important driving procedures and safety measures for drivers to follow on the road.
Uploaded by
PrevilageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
99 views10 pagesOral Lessons Manuscript
The document is a handbook on traffic signals and driving regulations in Zimbabwe, detailing various types of traffic signs, their meanings, and the rules associated with them. It also outlines the requirements for different vehicle licenses, including age limits and maximum speed limits for various vehicle classes. Additionally, it provides important driving procedures and safety measures for drivers to follow on the road.
Uploaded by
PrevilageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd