0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesUntitled Document
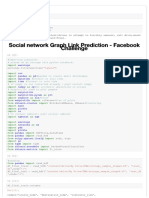
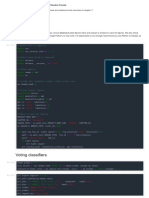
The document outlines a machine learning workflow using the Breast Cancer dataset, which includes feature selection through a neural network, training a Random Forest classifier, and optimizing its hyperparameters using a genetic algorithm. It evaluates the performance of both a normal and pruned Random Forest model, providing accuracy scores, confusion matrices, and classification reports. The process demonstrates the effectiveness of feature selection and optimization in improving model performance.
Uploaded by
aakashswastikunCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesUntitled Document
The document outlines a machine learning workflow using the Breast Cancer dataset, which includes feature selection through a neural network, training a Random Forest classifier, and optimizing its hyperparameters using a genetic algorithm. It evaluates the performance of both a normal and pruned Random Forest model, providing accuracy scores, confusion matrices, and classification reports. The process demonstrates the effectiveness of feature selection and optimization in improving model performance.
Uploaded by
aakashswastikunCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6