0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views5 pages4.2 SELF Controlled Mode: Rohini College of Engineering and Technology
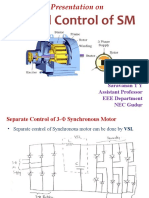
The document discusses the self-controlled mode of synchronous motors, where the supply frequency is adjusted to match the rotor speed, eliminating slip and hunting. It explains the operation of synchronous permanent magnet machines fed by inverters, highlighting their characteristics similar to DC motors and the use of load commutated inverters for efficient commutation. Additionally, it covers the control of power flow and regenerative braking through the manipulation of firing angles in converters, emphasizing the advantages of operating at a leading power factor.
Uploaded by
senthamilselvans.22eeeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views5 pages4.2 SELF Controlled Mode: Rohini College of Engineering and Technology
The document discusses the self-controlled mode of synchronous motors, where the supply frequency is adjusted to match the rotor speed, eliminating slip and hunting. It explains the operation of synchronous permanent magnet machines fed by inverters, highlighting their characteristics similar to DC motors and the use of load commutated inverters for efficient commutation. Additionally, it covers the control of power flow and regenerative braking through the manipulation of firing angles in converters, emphasizing the advantages of operating at a leading power factor.
Uploaded by
senthamilselvans.22eeeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd