0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesClssification of Parasites
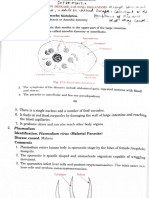
The document provides a classification of medically important parasites, detailing their species names, associated diseases, and key signs and symptoms. It categorizes parasites into protozoa, metazoa (including flatworms and roundworms), and describes their characteristics and life cycles. Additionally, it highlights the impact of these parasites on human health, including various diseases they cause.
Uploaded by
www.dazzi36736Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesClssification of Parasites
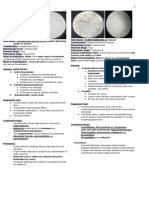
The document provides a classification of medically important parasites, detailing their species names, associated diseases, and key signs and symptoms. It categorizes parasites into protozoa, metazoa (including flatworms and roundworms), and describes their characteristics and life cycles. Additionally, it highlights the impact of these parasites on human health, including various diseases they cause.
Uploaded by
www.dazzi36736Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd