0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views10 pagesMemoryorg
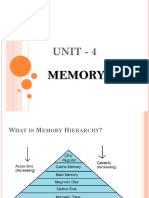
The document outlines the memory hierarchy in computers, detailing the roles of main memory, auxiliary memory, and cache memory. It explains the characteristics of RAM and ROM, highlighting their differences in terms of volatility, storage, and usage. Additionally, it describes the technology behind main memory, specifically focusing on static and dynamic RAM.
Uploaded by
Kamal RanniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views10 pagesMemoryorg
The document outlines the memory hierarchy in computers, detailing the roles of main memory, auxiliary memory, and cache memory. It explains the characteristics of RAM and ROM, highlighting their differences in terms of volatility, storage, and usage. Additionally, it describes the technology behind main memory, specifically focusing on static and dynamic RAM.
Uploaded by
Kamal RanniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd