0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views10 pagesValuation of Goodwill and Its Methods
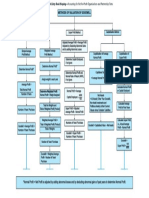
Goodwill is an intangible asset that represents a business's brand value, reputation, and customer loyalty, arising when a business is sold for more than its net assets. Valuing goodwill is important for business sales, mergers, and legal requirements, and various methods such as Average Profit, Super Profit, Capitalization, and Annuity can be used depending on the context. Accurate valuation of goodwill is essential for fair compensation during ownership changes.
Uploaded by
blinkssmeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views10 pagesValuation of Goodwill and Its Methods
Goodwill is an intangible asset that represents a business's brand value, reputation, and customer loyalty, arising when a business is sold for more than its net assets. Valuing goodwill is important for business sales, mergers, and legal requirements, and various methods such as Average Profit, Super Profit, Capitalization, and Annuity can be used depending on the context. Accurate valuation of goodwill is essential for fair compensation during ownership changes.
Uploaded by
blinkssmeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd