0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views2 pagesPermission
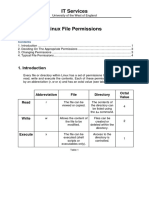
In Linux, permissions dictate access rules for files and directories, categorized into read, write, and execute types for three user categories: owner, group, and others. Permissions are displayed using the 'ls -l' command and can be modified with the 'chmod' command using either symbolic or numeric methods. The symbolic method uses operators to add, remove, or set permissions, while the numeric method employs octal codes to represent permission combinations.
Uploaded by
bhanupartap1125Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views2 pagesPermission
In Linux, permissions dictate access rules for files and directories, categorized into read, write, and execute types for three user categories: owner, group, and others. Permissions are displayed using the 'ls -l' command and can be modified with the 'chmod' command using either symbolic or numeric methods. The symbolic method uses operators to add, remove, or set permissions, while the numeric method employs octal codes to represent permission combinations.
Uploaded by
bhanupartap1125Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd