0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views7 pagesLinux Squid Config
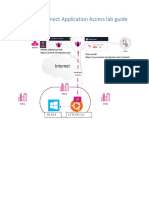
This document outlines the steps to configure GRE tunneling and Squid proxy on a CentOS system. It includes instructions for modifying SELinux settings, configuring network interfaces, managing iptables, and setting up Squid for WCCP. Additionally, it provides troubleshooting tips for verifying packet forwarding and Squid access logs.
Uploaded by
ThanosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views7 pagesLinux Squid Config
This document outlines the steps to configure GRE tunneling and Squid proxy on a CentOS system. It includes instructions for modifying SELinux settings, configuring network interfaces, managing iptables, and setting up Squid for WCCP. Additionally, it provides troubleshooting tips for verifying packet forwarding and Squid access logs.
Uploaded by
ThanosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd