0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views11 pagesChapter 3 MCQ
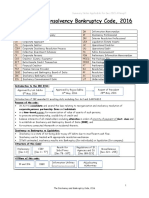
The document outlines key aspects of the Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) including the minimum default amount for initiating CIRP, who can initiate the process, and the roles of various parties involved. It details procedural steps such as the appointment of the Interim Resolution Professional, requirements for filing applications, and the voting shares needed for decisions by the Committee of Creditors. Additionally, it discusses the implications of resolution plans, liquidation triggers, and the legal framework surrounding these processes.
Uploaded by
t7u7s7h7a7r7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views11 pagesChapter 3 MCQ
The document outlines key aspects of the Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) including the minimum default amount for initiating CIRP, who can initiate the process, and the roles of various parties involved. It details procedural steps such as the appointment of the Interim Resolution Professional, requirements for filing applications, and the voting shares needed for decisions by the Committee of Creditors. Additionally, it discusses the implications of resolution plans, liquidation triggers, and the legal framework surrounding these processes.
Uploaded by
t7u7s7h7a7r7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd