0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views29 pagesDigital Circuits
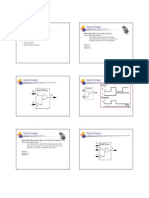
The document provides an overview of digital design fundamentals, focusing on electronic circuits, number systems, and conversion methods between different numeral systems. It explains the binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal systems, along with examples of conversions and arithmetic operations. Additionally, it introduces logic gates, including AND, OR, NOT, and NAND gates, with their respective truth tables and Boolean expressions.
Uploaded by
yy600opop77Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
71 views29 pagesDigital Circuits
The document provides an overview of digital design fundamentals, focusing on electronic circuits, number systems, and conversion methods between different numeral systems. It explains the binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal systems, along with examples of conversions and arithmetic operations. Additionally, it introduces logic gates, including AND, OR, NOT, and NAND gates, with their respective truth tables and Boolean expressions.
Uploaded by
yy600opop77Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd