0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesRevision Notes Computer Architecture
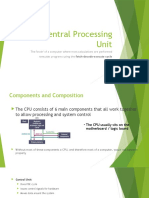
The document outlines the architecture and functions of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and microprocessors, detailing components such as the Control Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit, and system buses. It explains the Fetch, Decode, Execute cycle that the CPU uses to process instructions and highlights the importance of CPU performance factors like core count and clock speed. Additionally, it discusses the role of cache memory in enhancing CPU efficiency by storing frequently accessed data.
Uploaded by
RIHAAN GAWANDECopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesRevision Notes Computer Architecture
The document outlines the architecture and functions of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and microprocessors, detailing components such as the Control Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit, and system buses. It explains the Fetch, Decode, Execute cycle that the CPU uses to process instructions and highlights the importance of CPU performance factors like core count and clock speed. Additionally, it discusses the role of cache memory in enhancing CPU efficiency by storing frequently accessed data.
Uploaded by
RIHAAN GAWANDECopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd