0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views25 pagesECG For Nurses
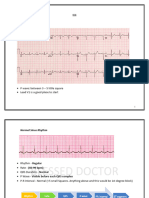
The document provides a comprehensive overview of ECG for nurses, covering basic concepts, the conduction system, and important measures. It details normal ECG readings, myocardial ischemia, and various arrhythmias including tachyarrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. The content emphasizes the significance of understanding ECG patterns for effective patient assessment and management.
Uploaded by
mahmoudbehharby377Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views25 pagesECG For Nurses
The document provides a comprehensive overview of ECG for nurses, covering basic concepts, the conduction system, and important measures. It details normal ECG readings, myocardial ischemia, and various arrhythmias including tachyarrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. The content emphasizes the significance of understanding ECG patterns for effective patient assessment and management.
Uploaded by
mahmoudbehharby377Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd