0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesOop 1
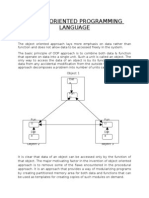
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a modular approach that organizes programs into objects, emphasizing data over procedures. Key features of OOP include encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and reusability, which allow for the creation of user-defined classes that bind data and functions together. Concepts such as compile-time and run-time polymorphism illustrate how operations can exhibit different behaviors based on the data types involved.
Uploaded by
Misiker DegafeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesOop 1
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a modular approach that organizes programs into objects, emphasizing data over procedures. Key features of OOP include encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and reusability, which allow for the creation of user-defined classes that bind data and functions together. Concepts such as compile-time and run-time polymorphism illustrate how operations can exhibit different behaviors based on the data types involved.
Uploaded by
Misiker DegafeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd