0% found this document useful (0 votes)
193 views5 pagesThe Elite Software Development Guide - From Zero To
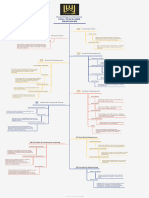
The Elite Software Development Guide outlines a structured pathway to becoming an elite software engineer, divided into four phases: Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced, and Elite, with a focus on clean code and human-centric design. It emphasizes mastering core programming concepts, code quality, security, testing, and the importance of collaboration and continuous learning. The guide also highlights the differences between human and AI coding practices, advocating for readability and simplicity in code.
Uploaded by
revena.inboxCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
193 views5 pagesThe Elite Software Development Guide - From Zero To
The Elite Software Development Guide outlines a structured pathway to becoming an elite software engineer, divided into four phases: Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced, and Elite, with a focus on clean code and human-centric design. It emphasizes mastering core programming concepts, code quality, security, testing, and the importance of collaboration and continuous learning. The guide also highlights the differences between human and AI coding practices, advocating for readability and simplicity in code.
Uploaded by
revena.inboxCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd