0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views6 pagesHA 5 Work Energy
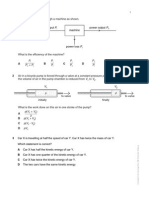
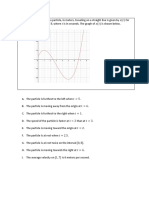
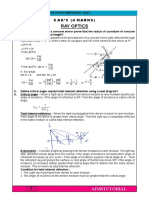
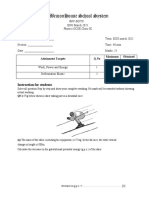
The document contains a series of physics problems and questions related to work, energy, and power, including calculations of potential and kinetic energy, efficiency, and work done in various scenarios. It features multiple-choice questions with options for answers, covering topics such as the motion of objects, energy conversion, and the principles of mechanics. The document also includes a section with answers to the questions provided.
Uploaded by
Manisa DasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views6 pagesHA 5 Work Energy
The document contains a series of physics problems and questions related to work, energy, and power, including calculations of potential and kinetic energy, efficiency, and work done in various scenarios. It features multiple-choice questions with options for answers, covering topics such as the motion of objects, energy conversion, and the principles of mechanics. The document also includes a section with answers to the questions provided.
Uploaded by
Manisa DasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd