0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views2 pagesMemory Vs Peripheral IO
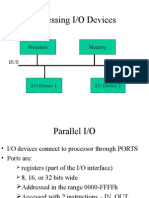
Memory-Mapped I/O shares the same address space as memory, allowing the use of standard memory instructions for I/O communication, but it can slow access and reduce usable memory space. In contrast, Peripheral-Mapped I/O uses a separate address space and special instructions for faster communication with I/O devices, without affecting memory space. The choice between the two methods depends on system requirements, such as the number of I/O ports and speed of communication.
Uploaded by
shivmandaluraniumCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views2 pagesMemory Vs Peripheral IO
Memory-Mapped I/O shares the same address space as memory, allowing the use of standard memory instructions for I/O communication, but it can slow access and reduce usable memory space. In contrast, Peripheral-Mapped I/O uses a separate address space and special instructions for faster communication with I/O devices, without affecting memory space. The choice between the two methods depends on system requirements, such as the number of I/O ports and speed of communication.
Uploaded by
shivmandaluraniumCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd