BDA-Chapter-2
HADOOP ARCHITECTURE
�HADOOP
• Hadoop is an Apache open source framework of tools, implemented in
JAVA and designed for storage and processing of large scale data (BIG DATA)
• Co-Founders were Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella in 2005
• Named after toy elephant of Doug Cutting’s son.
• In 2006, yahoo gave it to Apache Software.
• Who uses Hadoop? Netflix, Facebook, Amazon
• Hadoop has 2 components:
• i: HDFS
• ii: Mapreduce
�HDFS
• HDFS is designed to store and manage huge data in efficient manner.
• Only beneficial with large data
• Not Centralized but distributed storage.
�MapReduce
• It is a massive parallel processing technique for processing data.
• Big Data divided or distributed among various systems and then
parallel processing of data takes place
• Takes input in list format and provides output in the same way.
�Features of Hadoop
• Fault Tolerance: Replicates the files on nodes. Default replication is 3 times.
No duplication
(Replication=changes reflected in the files)
(Duplication=changes in master file do not reflect in copies)
• Highly Scalable: Number of nodes can be increased upto as many required
• Easy Programming: Where is data, how data is divided etc. Hides
Complexity from users.
• Huge and Flexible Storage: more nodes, more storage. Structured and
unstructured data both are available
• Low cost: open source framework
• Efficient: Bring Computation to nodes rather than data to nodes.
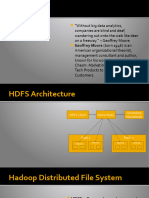
��Hadoop Architecture
• Hadoop has a Master-Slave Architecture for data storage and distributed data processing using MapReduce and HDFS methods.
• MapReduce: Massive parallel processing technique to process data. Takes and gives input/output in form of files.
• HDFS: Designed to store and manage huge amounts of data in an efficient manner
• Task Tracker: It Processes the small piece of data given to that particular node.
• NameNode: NameNode represents every files and directory which is used in the namespace. Keeps track about which information
is on which node.
• Namespace: A namespace is a set of signs (names) that are used to identify and refer to objects of various kinds. A namespace
ensures that all of a given set of objects have unique names so that they can be easily identified.
• DataNode: DataNode helps you to manage the state of an HDFS node and allows you to interacts with the block
• Job Tracker: Breaks the bigger tasks into pieces and forward it to the task tracker
• MasterNode: The master node allows you to conduct parallel processing of data using Hadoop MapReduce.
• Slave node: The slave nodes are the additional machines in the Hadoop cluster which allows you to store data to conduct complex
calculations. Moreover, all the slave node comes with Task Tracker and a DataNode. This allows you to synchronize the processes
with the NameNode and Job Tracker respectively.
��HDFS ECHOSYSTEM
• Used to store and manage data
• Key components in this layer are Data node and Name Node
• Name node keeps track of what information goes to which node.
• Also keeps the feature of replication working.
• Also keeps of information on replicated nodes
• Also keeps a track if any node is destroyed so now which node will
takes its place
• Data node has all data or information to be processed.
�HDFS Echosystem
• Hadoop Distributed File System follows the master-slave architecture.
• Each cluster comprises a single master node and multiple slave nodes.
• Internally the files get divided into one or more blocks, and each block is
stored on different slave machines depending on the replication factor
• The master node stores and manages the file system namespace, that is
information about blocks of files like block locations, permissions, etc.
• The slave nodes store data blocks of files.
�HDFS Echosystem
• Ex: If I have to find which video on Youtube has the most numbers of
views?
• Data stored in Data node and processing is done by task tracker.
• Youtube has a file.txt. This is divided into different blocks and nodes.
• Default block size in hadoop 1 is 64MB and that in Hadoop2 is 128MB
• Name node has all the information about which block is on which
node. It is the boss!
�HDFS Namenode
• NameNode is the centerpiece of the Hadoop Distributed File System.
• It maintains and manages the file system namespace and provides
the right access permission to the clients.
• The NameNode stores information about blocks locations,
permissions, etc. on the local disk in the form of two files:
• Fsimage: Fsimage stands for File System image. It contains the
complete namespace of the Hadoop file system since the NameNode
creation.
• Edit log: It contains all the recent changes performed to the file
system namespace to the most recent Fsimage.
�Functions of HDFS NameNode
• It executes the file system namespace operations like opening, renaming,
and closing files and directories.
• NameNode manages and maintains the DataNodes.
• It determines the mapping of blocks of a file to DataNodes.
• NameNode records each change made to the file system namespace.
• It keeps the locations of each block of a file.
• NameNode takes care of the replication factor of all the blocks.
• NameNode receives heartbeat and block reports from all DataNodes that
ensure DataNode is alive.
• If the DataNode fails, the NameNode chooses new DataNodes for new
replicas.
�HDFS Datanode
• DataNodes are the slave nodes in Hadoop HDFS.
• DataNodes are inexpensive commodity hardware.
• They store blocks of a file.
�Functions of DataNode
• DataNode is responsible for serving the client read/write requests.
• Based on the instruction from the NameNode, DataNodes performs
block creation, replication, and deletion.
• DataNodes send a heartbeat to NameNode to report the health of
HDFS.
• DataNodes also sends block reports to NameNode to report the list of
blocks it contains.
�HDFS Secondary Namenode
�HDFS Secondary Namenode
• Apart from DataNode and NameNode, there is another daemon called the secondary
NameNode.
• Secondary NameNode works as a helper node to primary NameNode but doesn’t replace primary
NameNode.
• When the NameNode starts, the NameNode merges the Fsimage and edit logs file to restore the
current file system namespace.
• Since the NameNode runs continuously for a long time without any restart, the size of edit logs
becomes too large. This will result in a long restart time for NameNode.
• Secondary NameNode solves this issue.
• Secondary NameNode downloads the Fsimage file and edit logs file from NameNode.
• It periodically applies edit logs to Fsimage and refreshes the edit logs. The updated Fsimage is
then sent to the NameNode so that NameNode doesn’t have to re-apply the edit log records
during its restart. This keeps the edit log size small and reduces the NameNode restart time.
• If the NameNode fails, the last save Fsimage on the secondary NameNode can be used to recover
file system metadata. The secondary NameNode performs regular checkpoints in HDFS.
�Checkpoint Node
• The Checkpoint node is a node that periodically creates checkpoints
of the namespace.
• Checkpoint Node in Hadoop first downloads Fsimage and edits from
the Active Namenode.
• Then it merges them (Fsimage and edits) locally, and at last, it uploads
the new image back to the active NameNode.
• It stores the latest checkpoint in a directory that has the same
structure as the Namenode’s directory.
• This permits the checkpointed image to be always available for
reading by the NameNode if necessary.
�Backup Node
• A Backup node provides the same check pointing functionality as the
Checkpoint node.
• In Hadoop, Backup node keeps an in-memory, up-to-date copy of the file
system namespace.
• It is always synchronized with the active NameNode state.
• It is not required for the backup node in HDFS architecture
to download Fsimage and edits files from the active NameNode to create a
checkpoint.
• It already has an up-to-date state of the namespace state in memory.
• The Backup node checkpoint process is more efficient as it only needs to
save the namespace into the local Fsimage file and reset edits.
• NameNode supports one Backup node at a time.
�Data Blocks
�Data Blocks
• Internally, HDFS split the file into block-sized chunks called a block.
The size of the block is 128 Mb by default. One can configure the
block size as per the requirement.
• For example, if there is a file of size 612 Mb, then HDFS will create
four blocks of size 128 Mb and one block of size 100 Mb.
• The file of a smaller size does not occupy the full block size space in
the disk.
• For example, the file of size 2 Mb will occupy only 2 Mb space in the
disk.
• The user doesn’t have any control over the location of the blocks.
�Replication Management
• For a distributed system, the data must be redundant to multiple places so that if
one machine fails, the data is accessible from other machines.
• In Hadoop, HDFS stores replicas of a block on multiple DataNodes based on the
replication factor.
• The replication factor is the number of copies to be created for blocks of a file
in HDFS architecture.
• If the replication factor is 3, then three copies of a block get stored on different
DataNodes. So if one DataNode containing the data block fails, then the block is
accessible from the other DataNode containing a replica of the block.
• If we are storing a file of 128 Mb and the replication factor is 3, then (3*128=384)
384 Mb of disk space is occupied for a file as three copies of a block get stored.
• This replication mechanism makes HDFS fault-tolerant.
�Rack Awareness
• Rack is the collection of around 40-50 machines (DataNodes) connected using the
same network switch. If the network goes down, the whole rack will be
unavailable.
• Rack Awareness is the concept of choosing the closest node based on the rack
information.
• To ensure that all the replicas of a block are not stored on the same rack or a
single rack, NameNode follows a rack awareness algorithm to store replicas and
provide latency and fault tolerance.
• Suppose if the replication factor is 3, then according to the rack awareness
algorithm:
• The first replica will get stored on the local rack.
• The second replica will get stored on the other DataNode in the same rack.
• The third replica will get stored on a different rack.
�HDFS Write Operation
• When a client wants to write a file to HDFS, it communicates to the NameNode for metadata.
• The Namenode responds with a number of blocks, their location, replicas, and other details.
• Based on information from NameNode, the client directly interacts with the DataNode.
• The client first sends block A to DataNode 1 along with the IP of the other two DataNodes where
replicas will be stored.
• When Datanode 1 receives block A from the client, DataNode 1 copies the same block to
DataNode 2 of the same rack.
• As both the DataNodes are in the same rack, so block transfer via rack switch.
• Now DataNode 2 copies the same block to DataNode 4 on a different rack.
• As both the DataNoNes are in different racks, so block transfer via an out-of-rack switch.
• When DataNode receives the blocks from the client, it sends write confirmation to Namenode.
• The same process is repeated for each block of the file.
�HDFS Read Operation
• To read from HDFS, the client first communicates with the NameNode for
metadata.
• The Namenode responds with the locations of DataNodes containing
blocks.
• After receiving the DataNodes locations, the client then directly interacts
with the DataNodes.
• The client starts reading data parallelly from the DataNodes based on the
information received from the NameNode.
• The data will flow directly from the DataNode to the client.
• When a client or application receives all the blocks of the file, it combines
these blocks into the form of an original file.
�Hadoop Echosystem
• Platform created to solve problems of Big Data
• It has a lot of tools that may help along with Hadoop to solve issues.
• 1. HDFS
• 2. MapReduce
• 3.Flume: Data ingestion tool in HDFS; fault tolerant
• 4.Hive: Open source data warehousing system for querying and analyzing large datasets stored in H.files. It uses HQL= Hive+SQL. It
is highly scalable
• 5.Hbase: Data is stored in Hadoop so if I run particular query, it might take some time. So Hbase is introduced. It is a distributed
column oriented database built on top of Hadoop File system. It is designed to process quick Random Access to huge amount of
data.
• 6.Mahout: Machine learning embedded on Big Data. It has 3 tasks;
Recommendation, Classification, Clustering
• 7. Pig: Data processing tool with own langaugae known as Pig Latin, scripting language
• 8. Sqoop: Imports Structured data from RDBMS to HDFS and vice versa export
• 9. Zookeeper: Keeps all features of Hadoop in together and coordinate among each other
�Hadoop Echosystem
�YARN
• Hadoop YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) is a Hadoop ecosystem component that provides the
resource management.
• Yarn is also one the most important component of Hadoop Ecosystem.
• YARN is called as the operating system of Hadoop as it is responsible for managing and monitoring
workloads.
• It allows multiple data processing engines such as real-time streaming and batch processing to handle data
stored on a single platform.
• Main features of YARN are:
• Flexibility – Enables other purpose-built data processing models beyond MapReduce (batch), such as
interactive and streaming. Due to this feature of YARN, other applications can also be run along with Map
Reduce programs in Hadoop2.
• Efficiency – As many applications run on the same cluster, Hence, efficiency of Hadoop increases without
much effect on quality of service.
• Shared – Provides a stable, reliable, secure foundation and shared operational services across multiple
workloads. Additional programming models such as graph processing and iterative modeling are now
possible for data processing.
�HIVE
• Apache Hive, is an open source data warehouse system for querying and analyzing large datasets
stored in Hadoop files.
• Hive do three main functions: data summarization, query, and analysis.
• Hive use language called HiveQL (HQL), which is similar to SQL. HiveQL automatically translates
SQL-like queries into MapReduce jobs which will execute on Hadoop.
• Main parts of Hive are:
• Metastore – It stores the metadata.
• Driver – Manage the lifecycle of a HiveQL statement.
• Query compiler – Compiles HiveQL into Directed Acyclic Graph(DAG).
• Hive server – Provide a thrift interface and JDBC/ODBC server.
• ODBC is a standard Microsoft Windows® interface that enables communication between database
management systems and applications typically written in C or C++.
• JDBC is a standard interface that enables communication between database management
systems and applications written in Oracle Java.
�PIG
• Apache Pig is a high-level language platform for analyzing and querying huge dataset
that are stored in HDFS.
• Pig as a component of Hadoop Ecosystem uses PigLatin language.
• It is very similar to SQL.
• It loads the data, applies the required filters and dumps the data in the required format.
• For Programs execution, pig requires Java runtime environment.
• Features of Apache Pig:
• Extensibility – For carrying out special purpose processing, users can create their own
function.
• Optimization opportunities – Pig allows the system to optimize automatic execution.
This allows the user to pay attention to semantics instead of efficiency.
• Handles all kinds of data – Pig analyzes both structured as well as unstructured.
�Hbase
• Apache HBase is a Hadoop ecosystem component which is a distributed database that was designed to store structured data in
tables that could have billions of row and millions of columns.
• HBase is scalable, distributed, and NoSQL database that is built on top of HDFS.
• HBase, provide real-time access to read or write data in HDFS.
• Components of Hbase
• There are two HBase Components namely- HBase Master and RegionServer.
• i. HBase Master
• It is not part of the actual data storage but negotiates load balancing across all RegionServer.
• Maintain and monitor the Hadoop cluster.
• Performs administration (interface for creating, updating and deleting tables.)
• Controls the failover.
• HMaster handles DDL operation.
• ii. RegionServer
• It is the worker node which handles read, writes, updates and delete requests from clients.
• Region server process runs on every node in Hadoop cluster. Region server runs on HDFS DateNode.
�HCatalog
• It is a table and storage management layer for Hadoop.
• HCatalog supports different components available in Hadoop ecosystems
like MapReduce, Hive, and Pig to easily read and write data from the
cluster.
• HCatalog is a key component of Hive that enables the user to store their
data in any format and structure. By default, HCatalog supports RCFile, CSV,
JSON, sequenceFile and ORC file formats.
• Benefits of HCatalog:
• Enables notifications of data availability.
• With the table abstraction, HCatalog frees the user from overhead of data
storage.
• Provide visibility for data cleaning and archiving tools.
�Mahout
• Mahout is open source framework for creating scalable machine learning algorithm and
data mining library. Once data is stored in Hadoop HDFS, mahout provides the data
science tools to automatically find meaningful patterns in those big data sets.
• Algorithms of Mahout are:
• Clustering – Here it takes the item in particular class and organizes them into naturally
occurring groups, such that item belonging to the same group are similar to each other.
• Collaborative filtering – It mines user behavior and makes product recommendations
(e.g. Amazon recommendations)
• Classifications – It learns from existing categorization and then assigns unclassified items
to the best category.
• Frequent pattern mining – It analyzes items in a group (e.g. items in a shopping cart or
terms in query session) and then identifies which items typically appear together.
�Sqoop
• Sqoop imports data from external sources into related Hadoop ecosystem components
like HDFS, Hbase or Hive.
• It also exports data from Hadoop to other external sources.
• Sqoop works with relational databases such as teradata, Netezza, oracle, MySQL.
• Features of Apache Sqoop:
• Import sequential datasets from mainframe – Sqoop satisfies the growing need to move
data from the mainframe to HDFS.
• Import direct to ORC files – Improves compression and light weight indexing and
improve query performance.
• Parallel data transfer – For faster performance and optimal system utilization.
• Efficient data analysis – Improve efficiency of data analysis by combining structured data
and unstructured data on a schema on reading data lake.
• Fast data copies – from an external system into Hadoop.
�Flume
• Flume efficiently collects, aggregate and moves a large amount of
data from its origin and sending it back to HDFS.
• It is fault tolerant and reliable mechanism.
• It allows the data flow from the source into Hadoop environment.
• It uses a simple extensible data model that allows for the online
analytic application.
• Using Flume, we can get the data from multiple servers immediately
into hadoop.
�Zookeeper
• Apache Zookeeper is a centralized service and a Hadoop Ecosystem
component for maintaining configuration information, naming,
providing distributed synchronization, and providing group services.
Zookeeper manages and coordinates a large cluster of machines.
• Features of Zookeeper:
• Fast – Zookeeper is fast with workloads where reads to data are more
common than writes. The ideal read/write ratio is 10:1.
• Ordered – Zookeeper maintains a record of all transactions.