0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesSQL Different Statement Queries
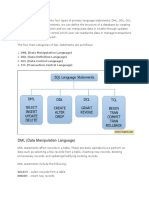
The document outlines the four main types of SQL statements: Data Definition Language (DDL) for managing database structure, Data Manipulation Language (DML) for handling data within tables, Data Control Language (DCL) for managing user permissions, and Transaction Control Language (TCL) for controlling transaction processes. Each type includes specific commands with defined purposes, such as creating, modifying, or deleting database objects, manipulating data, managing access controls, and ensuring data integrity during transactions. Examples of commands for each category are provided, illustrating their functionality.
Uploaded by
Swastik PradhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesSQL Different Statement Queries
The document outlines the four main types of SQL statements: Data Definition Language (DDL) for managing database structure, Data Manipulation Language (DML) for handling data within tables, Data Control Language (DCL) for managing user permissions, and Transaction Control Language (TCL) for controlling transaction processes. Each type includes specific commands with defined purposes, such as creating, modifying, or deleting database objects, manipulating data, managing access controls, and ensuring data integrity during transactions. Examples of commands for each category are provided, illustrating their functionality.
Uploaded by
Swastik PradhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd