Math Lab Activities – Class 10 (2025–
26)
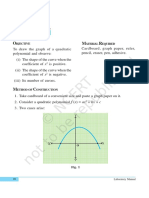
Activity 1: Graph of a Quadratic Polynomial
Objective
To draw the graph of a quadratic polynomial and observe:
(i) Shape when the coefficient of x² is positive
(ii) Shape when it's negative
(iii) Number of zeroes
Materials Required
Graph paper, pencil, ruler, table of values
Theory
A quadratic polynomial is of the form y = ax² + bx + c. If a > 0, the parabola opens upwards;
if a < 0, it opens downwards. The graph may intersect the x-axis at 0, 1, or 2 points (zeroes).
Procedure
1. Take equations: y = x² – 4 and y = –x² + 4
2. Create tables of values
3. Plot the graphs on graph paper
4. Observe the shape and number of x-intercepts
Diagram
Draw two parabolas (upward and downward opening) on the graph.
Observations
y = x² – 4 opens upward, cuts x-axis at two points
y = –x² + 4 opens downward, also cuts at two points
Result
Graph of a quadratic is a parabola. The number of zeroes = number of x-axis intersections.
Applications
Projectile motion, bridge designs, parabolic reflectors
Activity 2: Consistency of Linear Equations (Graphical Method)
Objective
�To verify consistency/inconsistency of a pair of linear equations by graph.
Materials Required
Graph paper, ruler, pencil
Theory
Two linear equations:
- Intersecting → one solution (consistent)
- Parallel → no solution (inconsistent)
- Coincident → infinite solutions (consistent)
Procedure
1. Choose 3 pairs of equations (one each for all three cases)
2. Make tables of values
3. Plot and draw the lines on graph paper
4. Observe their intersection behavior
Diagram
Draw 3 graphs: intersecting, parallel, and coincident lines.
Observations
Each pair demonstrates a different case of consistency.
Result
Graph confirms if equations are consistent or inconsistent.
Applications
Used in solving real-life constraint-based problems.
Activity 3: Solving Quadratic Equation Geometrically
Objective
To solve the equation x² + 4x = 60 by completing square geometrically.
Materials Required
Paper, ruler, pencil, compass
Theory
Completing the square converts x² + 4x = 60 into a perfect square.
Procedure
1. Rewrite: x² + 4x = 60
2. Add 4 to both sides ⇒ x² + 4x + 4 = 64
3. (x + 2)² = 64 ⇒ x = –2 ± 8 ⇒ x = 6 or –10
�Diagram
Draw square and rectangles to demonstrate the square completion.
Observations
The roots of the quadratic are x = 6, –10
Result
Roots found geometrically using completing square method.
Applications
Used in physics, geometry, and optimization problems.
Activity 4: Identifying Arithmetic Progressions (APs)
Objective
To identify arithmetic progressions in number patterns.
Materials Required
Paper and pen
Theory
An AP has a common difference d = a₂ – a₁ = a₃ – a₂
Procedure
1. Take number sequences
2. Subtract consecutive terms
3. If difference is same, it's an AP
Diagram
Not required
Observations
Patterns with equal differences are APs
Result
Identified APs using common difference.
Activity 5: Sum of First n Natural Numbers
Objective
To derive the formula for the sum of first n natural numbers.
�Materials Required
Chart paper, marker
Theory
Sum = n(n + 1)/2
Procedure
1. Arrange numbers 1 to n forward and backward
2. Add corresponding terms
3. Total sum = n(n + 1)/2
Diagram
Not required
Observations
Sum matches for values like n = 5, 10, etc.
Result
Verified sum = n(n + 1)/2.
Activity 6: Sum of First n Odd Natural Numbers
Objective
To find the sum of first n odd natural numbers.
Theory
Sum = n²
Procedure
1. List first n odd numbers: 1, 3, 5, ...
2. Count and sum
3. Compare with n²
Diagram
Not required
Observations
Sum of first 3 odd numbers = 9 = 3²
Result
Verified sum = n²
�Activity 7: Sum of First n Even Natural Numbers
Objective
To find the sum of first n even natural numbers.
Theory
Sum = n(n + 1)
Procedure
1. List first n even numbers
2. Add them
3. Compare with n(n + 1)
Diagram
Not required
Observations
Sum of first 4 even numbers = 20 = 4×5
Result
Verified sum = n(n + 1)
Activity 8: Formula for Sum of AP
Objective
To establish the formula Sn = n/2[2a + (n – 1)d]
Procedure
1. Consider AP: a, a + d, a + 2d, ...
2. Write sum forward and backward
3. Add them to derive the formula
Result
Sum formula for AP verified algebraically and numerically.
Activity 10: Basic Proportionality Theorem
Objective
To verify that a line parallel to one side of triangle divides other two sides in same ratio.
�Procedure
1. Draw triangle ABC
2. Draw DE || BC
3. Measure and compare ratios: AD/DB and AE/EC
Result
Verified that DE divides AB and AC proportionally.
Activity 11: Verifying Distance Formula
Objective
To verify distance formula graphically.
Procedure
1. Plot points A and B
2. Form right triangle with base and height
3. Use Pythagoras Theorem
Result
Distance between points matches formula.
Activity 12: Verifying Section Formula
Objective
To verify section formula graphically.
Procedure
1. Plot A(x₁, y₁), B(x₂, y₂)
2. Divide AB in m:n
3. Calculate coordinates and verify
Result
Point dividing line segment matches formula.
Activity 13: Finding Height Using Clinometer
Objective
To find the height of a building using trigonometry.
�Procedure
1. Measure distance from building
2. Use clinometer to measure angle
3. Height = base × tan(angle)
Result
Height of object found using trigonometry.
Activity 15: Tangent is Perpendicular to Radius
Objective
To verify that a tangent to a circle is ⟂ to the radius.
Procedure
1. Draw circle and tangent at point P
2. Draw radius OP
3. Measure ∠between OP and tangent
Result
Tangent is perpendicular to radius.
Activity 17: Area of Circle (Experimental)
Objective
To derive area formula of circle experimentally.
Procedure
1. Cut circle into sectors
2. Rearrange to form rectangle
3. Area = πr²
Result
Derived formula: Area = πr²
Activity 20: Experimental Probability Using a Die
Objective
To determine experimental probability of die outcomes.
�Procedure
1. Throw die 500 times
2. Record outcomes
3. Calculate frequency/500 for each
Result
Experimental probabilities approximate theoretical values.