0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views5 pagesLets Know The Comparison of RT
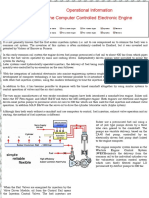
The document compares MC, RT-flex, and ME marine diesel engines, highlighting their differences in fuel injection, exhaust valve control, and automation systems. The MC engine features mechanical control with fixed injection timing, while RT-flex and ME engines utilize electronic control with variable injection timing for improved efficiency and lower emissions. Overall, the evolution from MC to RT-flex and ME represents a shift from mechanical to digital control, leading to better performance and fuel flexibility.
Uploaded by
ma12.ma863Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views5 pagesLets Know The Comparison of RT
The document compares MC, RT-flex, and ME marine diesel engines, highlighting their differences in fuel injection, exhaust valve control, and automation systems. The MC engine features mechanical control with fixed injection timing, while RT-flex and ME engines utilize electronic control with variable injection timing for improved efficiency and lower emissions. Overall, the evolution from MC to RT-flex and ME represents a shift from mechanical to digital control, leading to better performance and fuel flexibility.
Uploaded by
ma12.ma863Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd