0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageCysts
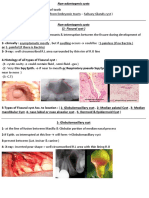
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can be classified as true or false based on its epithelial lining. Cysts can be congenital or acquired, with various types including retention, implantation, and neoplastic cysts, and they may lead to complications such as torsion, hemorrhage, and infection. Treatment options include excision, marsupialization, and drainage.
Uploaded by
Kaung KhantCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageCysts
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can be classified as true or false based on its epithelial lining. Cysts can be congenital or acquired, with various types including retention, implantation, and neoplastic cysts, and they may lead to complications such as torsion, hemorrhage, and infection. Treatment options include excision, marsupialization, and drainage.
Uploaded by
Kaung KhantCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd