0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views6 pagesExp 2
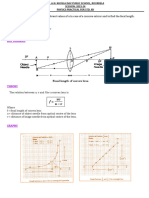
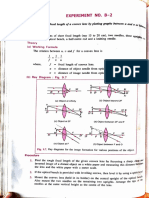
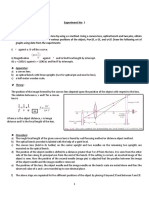
The document outlines an experimental procedure to determine the focal length of a convex lens using an optical bench and various measurements. It details the setup, measurements, calculations, and graphing methods to analyze the relationship between object distance (u), image distance (v), and focal length (f). The document also includes precautions to ensure accurate results during the experiment.
Uploaded by
Mars JOJO444Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views6 pagesExp 2
The document outlines an experimental procedure to determine the focal length of a convex lens using an optical bench and various measurements. It details the setup, measurements, calculations, and graphing methods to analyze the relationship between object distance (u), image distance (v), and focal length (f). The document also includes precautions to ensure accurate results during the experiment.
Uploaded by
Mars JOJO444Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd