0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views11 pagesFunctions in Excel
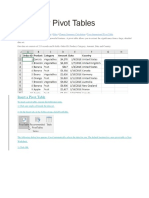
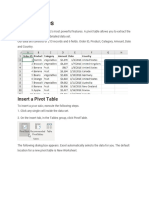
The document provides an overview of HLOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions in Excel, highlighting key points such as case insensitivity, the requirement for the lookup value to be in the topmost row, and error handling. It also explains how to create and manipulate pivot tables, including inserting them, sorting, filtering, and changing summary calculations. Additionally, it covers the creation of pivot charts and their connection to pivot tables, along with instructions for filtering and changing chart types.
Uploaded by
aasimshaikh376Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views11 pagesFunctions in Excel
The document provides an overview of HLOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions in Excel, highlighting key points such as case insensitivity, the requirement for the lookup value to be in the topmost row, and error handling. It also explains how to create and manipulate pivot tables, including inserting them, sorting, filtering, and changing summary calculations. Additionally, it covers the creation of pivot charts and their connection to pivot tables, along with instructions for filtering and changing chart types.
Uploaded by
aasimshaikh376Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd