0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views4 pagesAliphatic Compounds Reviewer
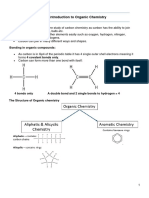
The document provides a comprehensive overview of aliphatic compounds, including their structure, naming conventions, and functional groups. Key points include the importance of numbering carbon chains, identifying branches, and understanding the impact of branching on hydrogen counts. It also covers IUPAC naming rules and examples of complex compound names, emphasizing the significance of functional groups in determining reactivity.
Uploaded by
erichchloe2311Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views4 pagesAliphatic Compounds Reviewer
The document provides a comprehensive overview of aliphatic compounds, including their structure, naming conventions, and functional groups. Key points include the importance of numbering carbon chains, identifying branches, and understanding the impact of branching on hydrogen counts. It also covers IUPAC naming rules and examples of complex compound names, emphasizing the significance of functional groups in determining reactivity.
Uploaded by
erichchloe2311Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd