1.
Differentiate Analog and Digital and give at least 1 example
- The main difference between analog and digital lies in how they represent information:
Analog:
Continuous: Values change smoothly and gradually over time, with infinitely many possibilities within a range. Imagine
the smooth curve of a sound wave.
Examples:
Temperature readings on a thermometer (e.g., 23.5°C)
Digital:
Discrete: Values exist only at specific points, like steps on a ladder. Think of a square wave with clear on/off states.
Examples:
Temperature displayed on a digital thermometer (e.g., 23°)
2. Differentiate SMS and MMS
'SMS' stands for 'Short Message Service', a service of text-based messages between limited-length mobile devices up to
160 characters of one message. It presents a universal channel that can be used on all kinds of mobile devices and can
be accessible and supported on all networks in the world. On the contrary, MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service)
extends SMS to a message that could contain multimedia contents that are images, videos, and audio files, alongside
long text messages. MMS requires a data connection and is commonly used for sharing richer media content between
mobile users.
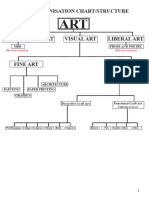
1. what are the principles of graphic and visual/communication design?
Graphic and visual communication design offers a set of principles that guide one in how to
create an effective and beautiful visual composition. Some of these include:
Balance: Distribution of the elements of the design can be a great way to create stability and
harmony. The balance can either be symmetrical.
Hierarchy: Yes, indeed, hierarchy organizes all elements in a design to guide the viewer on
what to look at and communicate the importance of all elements in it. This is done through
techniques such as size, color, contrast, and placement to clearly indicate a visual order.
Contrast: Contrast uses opposites, for example in the use of color, size, shape or texture to
create difference, thereby gain emphasis or more interest. It helps in bringing out the most
important element and aids in readability.
Emphasis: Emphasis denotes a central area or key things within a design bringing the attention
of the viewer and communicating the needed message. It can be brought out by means of
contrast, color, size, placement, or use of typography.
Repetition: Repeating elements can generate a design with a certain level of unity or
consistency. This may be done through color, shape, or pattern. It reinforces the overall aesthetic
and serves in developing a sense of visual rhythm.
Alignment: Refers to the position of elements in a design in relation to one another in order to
create a cohesive and organized layout. It increases the visual association between elements
and therefore promotes clarity and legibility.
Proximity is used to group related elements together within a design to have them visually
connected for asserting their relationship with each other. It helps a person keep organized with
information and makes the design more readable and comprehensible.
�By applying these principles effectively, design works may be made visually appealing,
comprehensible, and may thoroughly bring out the intended message to the audience.
2. what are the characteristics of digital and traditional graphics?
The method for getting digital images is by means of scanners or digital cameras, whereas the
traditional method of getting graphics is by means of cameras and scanning gadgets.
Characteristics of digital graphics graphics
Flexibility: The concept of high flexibility includes an easy manipulation process, with countless
inclusions of editing and modifications exercised through different software tools. What is more
important is that changes can be brought quickly and easily, and it does not affect the original
artwork.
Scale-independent: In digital graphics, one can adjust the size of the picture into any scale
without affecting the quality of the picture. This makes digital graphics very handy because the
pictures can be used in small icons or even big billboards.
Precision: Digital graphics allow control to be excised over such elements as lines, shapes,
color, and typography to the highest of exactitude. Designers achieve fine detail and precise
placements, both of which contribute to the final appearance of the artwork looking professional
and polished.
Interactivity: In digital graphics, interactivity, animation, and multimedia add-ons can be
included in various elements to raise involvement levels of the user and to make the graphics
time-based. It functions very efficiently in electronic means such as websites, mobile
applications, and multimedia presentations.
Accessibility: Digital graphics may be easily distributed and accessed online with much ease, in
order to reach a large global audience across diverse devices and platforms. What's more, the
pieces of work may easily be shared, downloaded, or printed out, meaning that there is really a
great deal of simplicity when it comes to collaboration in the pieces of artwork.
Characteristics of traditional graphics
Tactile: Traditional graphics are intrinsically tactile and can, therefore, be taken in one's hands
and felt, since they are materials upon or through which they are produced—paper, canvas, ink,
paint, and the like—or the analogs of these materials. Tactile means that it is possible to touch it.
Unique Texture: In traditional graphics, the unique texture and characteristics usually emerge
from the specific art mediums and techniques in a particular work. The textures so obtained are
rich and deep, thus creating an appealing visual in which one is felt to be touching and sensing
it.
Handmade Quality: Traditional graphics usually stimulate feelings of handcrafted quality and
feelings of originality in regard to their origin because of realization through skills and technique.
Each piece of traditional graphic work is basically unique and has its own soul—something of the
hand of its creator—thereby reinforcing artistic value.
Time-Consuming: This involves in-depth planning and preparation, along with traditional
graphic execution that may involve a single piece of artwork over the course of an entire day or
even weeks.
Physical Limitations: There are common characteristics that are related to physical limitations
for traditional graphics, such as size, strength, and preservation. Special materials and tools
might be needed to create large-scale artwork, whereas delicate mediums might be damaged or
deteriorate over some time.
In short, digital and traditional graphics both have their distinct characteristics and advantages,
�and both carry with them their own value and are appreciated separately for the artistic
expression, the creativity, and visual impact that is offered by such tools.
3. discuss the color theory
- The color theory represents an important concept in arts, design, and many other spheres of
life, including the perception of the interaction between human beings and colors in arousing
emotions. Here are some key elements related to the theory of color:
Color Wheel: A visual placement of the color associations is being given in the form of a color
wheel, usually with primary colors (red, blue, and yellow), secondary colors (orange, green, and
purple), and tertiary colors (formed by the blend of a primary and a secondary color). Color
wheel and its arrangement help to understand the harmonies and contrasts of colors.
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Colors: Primary colors form the base of the theory of color,
and these colors cannot be created by the combination of any other colors. The secondary colors
result from the combination of two primary colors, while the tertiary colors are formed when a
secondary color is added to a primary color. Understanding these relations amongst the colors
then is the beginning of color mixing and consequently the essential core of color harmony.
Color Harmony: Color harmony refers to the pleasing arrangement of colors in a composition.
All will lead to different visual effects and moods, through the different color harmonies,
including complementary (which is the opposite colors on the color wheel), analogous (which are
adjacent colors), and triadic (which is three evenly spaced colors on the color wheel). Color
harmony in designs and visual arts is a key undertaking to establish.
Warm and Cool: Colors can generally be divided as either warm or cool based on their apparent
temperature. Warm colors (red, orange, yellow) convey energy, warmth, and liveliness. Opposing
(blue, green, purple) is cool, calm, and quiet. Understanding color temperature helps in creating
mood and atmosphere in artworks and designs.
Psychology of colors: Colors play a psychological role in emotions and human behavior. For
example, it is real that red has multiple symbolic meanings such as passion, exciting, and
dangerous, while blue represents serenity, confidence, and stability. The choice of colors can
thus affect perceptions, evoke emotions, and provide common messages in works of art,
designs, branding, and even marketing.
Contrast of Color: It is the contrast between the differences in color value, hue, and saturation
between elements in a composition. A strong contrast will give a visual dynamic punch to certain
elements and a weak contrast will give a more low-key, unified effect. Understanding color
contrast is crucial in creating hierarchy, readability, and visual impact in designs.
Color theory enables one as an artist, a designer, or creator to know how best to use colors and
their properties to communicate, show sentiments, and offer great visual impact on the given
medium one is applying the knowledge to—paint, graphics, interiors, or other creative formats.
After all, color theory is merely one more instrument for the creation of those bright and
harmonic compositions—either in the form of paintings, graphics, or interiors.