0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views20 pagesFractals - Class Presentation
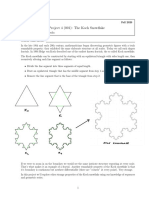
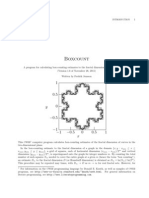
Fractals are complex images generated by computer algorithms through iterative processes, characterized by self-similarity and infinite detail. The document discusses the Sierpinski Triangle as an example of fractal creation, illustrating the iterative steps involved in its formation. Additionally, it highlights the applications of fractals in various fields such as astronomy and biology, and explains the concept of fractal dimensions and their implications on perimeter and area.
Uploaded by
Kakshil VajaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views20 pagesFractals - Class Presentation
Fractals are complex images generated by computer algorithms through iterative processes, characterized by self-similarity and infinite detail. The document discusses the Sierpinski Triangle as an example of fractal creation, illustrating the iterative steps involved in its formation. Additionally, it highlights the applications of fractals in various fields such as astronomy and biology, and explains the concept of fractal dimensions and their implications on perimeter and area.
Uploaded by
Kakshil VajaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd