0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pagesPB1170
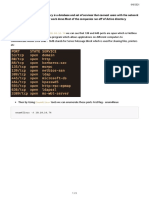
The document outlines the lifecycle of the PB1170 Kerberoasting project, which is currently in development. It includes details about the project manager, key dates for simulation and configuration changes, and methodologies for both attack and defense against Kerberoasting. Additionally, it highlights lessons learned regarding privilege escalation risks and the importance of using honey accounts for detection.
Uploaded by
swapan555Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views2 pagesPB1170
The document outlines the lifecycle of the PB1170 Kerberoasting project, which is currently in development. It includes details about the project manager, key dates for simulation and configuration changes, and methodologies for both attack and defense against Kerberoasting. Additionally, it highlights lessons learned regarding privilege escalation risks and the importance of using honey accounts for detection.
Uploaded by
swapan555Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd