0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesOSM SeniorF 03 Sol e
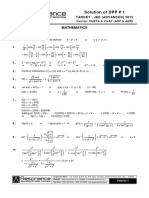
The document contains solutions to exercises related to basic functions, polynomial equations, and transformations of functions. It includes calculations and derivations for various function values and parameters, demonstrating the application of algebraic principles. The exercises are structured to reinforce understanding of function behavior and manipulation.
Uploaded by
某某Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesOSM SeniorF 03 Sol e
The document contains solutions to exercises related to basic functions, polynomial equations, and transformations of functions. It includes calculations and derivations for various function values and parameters, demonstrating the application of algebraic principles. The exercises are structured to reinforce understanding of function behavior and manipulation.
Uploaded by
某某Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd