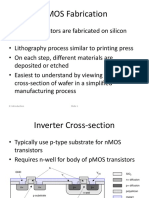
MOS Processing
Oxide etch Grown of materials Substrate Substrate
UV
Mask Resist
Final layer pattern
Substrate Substrate
�CMOS Process Flow
Semiconductor manufacturing companies developed highly advanced processing techniques Details of their process flows are highly proprietary and hence secretive
�Starting Wafer with Epitaxial Layer
Starting point is a p+ wafer with a thin p-type epitaxial layer of silicon grown on top Epitaxial layer is created by dropping silicon atoms onto a heated wafer to form a high quality crystal layer for transistor
p-epitaxial layer p+ substrate
�Formation of n-well Regions using a masking step
This defines the location of PMOS
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
�Active Area Definition Using Nitride/Oxide
Every transistor is built in an active area Active areas are defined by a masking step that patterns a layer of silicon nitride that rests on a thin layer of thermal oxide
Nitride
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
�Electrical Isolation
Nitride pattern is used to define silicon etched regions Oxide is then grown or deposited in the etched regions
Etched regions
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
�Field Oxide Growth
Field oxide
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
�Poly Gate Deposition and Patterning
Poly
Poly
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
�P Select Mask and Implant
Boron implant
Resist
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
p+ implants
�N Select Mask and Implant
Arsenic implant
Resist
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
n+ implants
�CVD Oxide Is Grown
CVD Oxide
p-epitaxial layer
n-well
�Interconnections
After CVD oxide active contact, W plugs
CVD Oxide n-well
p-epitaxial layer
�Metal1 Coating and Patterning
Metal1
CVD Oxide n-well
p-epitaxial layer
�Bonding Pad Structure
After all metal layers have been added, the entire chip is covered with nitride It is an insulator so a via must be etched to gain electrical access to the chip To interface with the outside world is to use a pad frame arrangement Large metal bonding pads surround the central chip core area Wires are attached between the pads and the output pins of the package
�Bonding Pad Structure
Metal pad
Overglass
Wire
To package pin
Overglass Cut
Bond Metal bonding pad
Top view
To silicon
Side view
�Bonding Pad
Pad to outside wire connection
�Variations
Lightly doped drain and source Slicides (Si + Pt) The use of copper as an interconnect material
�Copper As Interconnection
The resistivity of copper is one-half of aluminum It cannot be patterned using standard technique It is very difficult to etch It diffuses very rapidly through silicon and can alter the electrical characteristics
�Copper Patterning Using the Damascene Process
Oxide trenches for copper patterns SiO2 Wafer Cu
SiO2 Wafer Copper deposition
SiO2 Wafer After planarization
�Ohmic Contact of CMOS
Ohmic contact Ohmic contact
Vss
B p+ S n+
V in
D n+ NMOS transistor PMOS transistor p-substrate
DD
V o
D p+ n-well
S p+
B n+
�CMOS Inverter Processing Technology in 3D
�CMOS Processing Technolog
�CMOS Processing Technology
�CMOS Processing Technology
�CMOS Processing Technology
�CMOS Latchup
Latchup is the condition in which the paracitic components give rise to the establishment of low resistance conducting paths between VDD and Ground. The CMOS structure contains parasitic bipolar transistors that have the potential to destroy the CMOS circuitry.
�CMOS Latchup
If VRsub is 0.7V
V
B p+
SS
If VRwell is 0.7V
(0 V)
D n+
V
D p+ p+ S
DD
(5 V)
B
S n+
n+
npn transistor Rsub
n-well
Rwell
p-type substrate
pnp transistor
�Preventing latch-up
An increase in the substrate doping levels with consequent drop in the value of Rsub Reducing Rwell by control fabrication params by ensuring a low contact resistance to Vss Guard Ring (out of scope of our study)
�Thank You