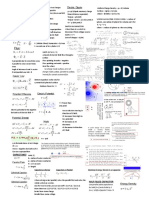
The energy stored is (1/2)CV^2
Power= V^2/r
F(12)= by q1 on q2
If Elec F is only F then particle accelerating A=(q/m)E
Parallel conducting plates The field is E = V/d = 12/0.004 = 3000 V/m = 3000 N/C force of charge in field = Eq
�Work place 3 charges W(q1)=0 W(q2)=q(2)xV =q(2)xkq(1)/r W(q3=q(3)((kq(1)/r+kq(2)/r Wtot=w3+w2
Electric potential V V is path independent V=kq/r
The negative plate is at the lower potential if we are using the classical reference that current (not electrons) flows from positive to negative. The work done by the electric field is the force on the electron times the distance it is moved through
Linear charge density electric field E(y)= kQ/(y*sqrt((L/2)^2+y^2)) E(x)=kq/(x(o)(x(o)-L)) kQ/x^2 (point part)
Outward flux ? = EAx/2
Flux = enclosed charge/E(o))
+ A charge is placed uniformly on a square sheet nonconducting on yz plane: Surface charge density = Q/A Mag of [Link] to right and left of sheet E=s/2E(o)
C=S/d is the initial capacitance of the parallel-plate capacitor C1=S/(d+d) is the capacitance after moving the plates U=Q/C U+U=Q/C1 is the voltage after moving the plates ==> Qd/(S)+U=Q(d+d)/(S) ==> U=Q*d/(S) Q=S*U/d (b) W=0.5QU initial energy W1=0.5Q(U+U) W=W1-W=0.5Q*U
SPEED FRM ORIGIN The distance from each point to the origin is a*sqrt(2) so V = k*q/r so we get V = k/(a*sqrt(2))*(q + 2q -3q+6q) = 6/sqrt(2)*(kq/a) = 4.24*k*q/a so the potential energy = V*q = 4.24*k*q^2/a At infinity this potential energy is now kinetic 1/2*m*v^2 = 4.24*k*q^2/a so v = sqrt(2*4.24*k*q^2/(m*a)) = sqrt(8.48*k*q^2/(m*a))
if the electric field is 0 in some region of space, the electric potential must also be 0 in that region FALSE If the electric potential is 0 in some region of space, the electric field must also be 0 in that region TRUE If the electric potential is 1 at a point, the electric field must also be0 at that point FALSE Electric field lines always point toward regions of lower potential TRUE The value of the electric potential can be chosen to be 0 at any convenient point TRUE Dielectric breakdown occurs in the air when the potential is 3*10^6 V true
Electric flux = EA when Elec Field is perp to AreaNot perp =EAcos()
For curved surface delta =EdeltaAcos()
When the side is perp to field there is no flux