0% found this document useful (0 votes)
476 views38 pagesIntermediate Excel Workshop Guide
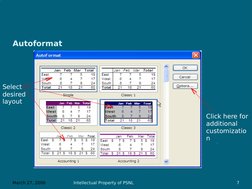
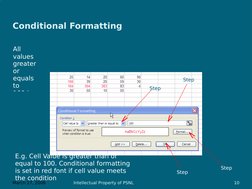
This document outlines objectives and content for an Intermediate Excel workshop. The workshop will cover advanced formatting techniques like customizing toolbars, autoformatting, using the format painter, and conditional formatting. It will also cover functions, formulas, and cell references. Additional topics include managing workbooks through techniques like freezing panes, headers and footers, linking sheets, protecting workbooks, and saving as a workspace. Formatting tools, functions, formulas, and managing workbooks are the key skills that will be covered in the intermediate Excel workshop.
Uploaded by
asticksCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
476 views38 pagesIntermediate Excel Workshop Guide
This document outlines objectives and content for an Intermediate Excel workshop. The workshop will cover advanced formatting techniques like customizing toolbars, autoformatting, using the format painter, and conditional formatting. It will also cover functions, formulas, and cell references. Additional topics include managing workbooks through techniques like freezing panes, headers and footers, linking sheets, protecting workbooks, and saving as a workspace. Formatting tools, functions, formulas, and managing workbooks are the key skills that will be covered in the intermediate Excel workshop.
Uploaded by
asticksCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd