MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING
BY APRAJITA MALHAN (32)
BHARTI SINGH (44)
(MBA A)
CONTENTS
1. Introduction
2. Principles of management accounting
3. Need of management accounting
4. Functions
5. Scope
6. Tools & techniques
7. Importance
8. Limitation
9. Professional characteristics of a managerial accountant
10. Management v/s financial accounting
INTRODUCTION
Managerial Accounting is the process of tracking, recording
and examining costs associated with the products or actions
of an association.
Managerial accounting does not track normally
acknowledged accounting principles. In managerial
accounting, costs are considered in units of currency by
convention.
Managerial accounting can also be defined as a kind of cost
accounting that convert the supply chain into economic
values. Supply chain is nothing but the sequence of events in
the manufacture process which results in a product.
Managers mostly use cost accounting principles to maintain
alternative making to reduce companys expenses and
progress its productivity.
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGERIAL
ACCOUNTING
Strategic - Preceding the role of the organization
accountant as a strategic co-worker in the association.
Performance management - Improves business by
managing and evaluating and thereby giving the
performance of the company.
Risk Management - Concentrates on frameworks and
practices for recognizing, managing and reporting risks to
the achievement of the objectives of the organization
NEED OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
1. PLANNING
The plans of management are often expressed
formally in budgets
Term budgeting is applied to generally describe the
planning process
Budgets are usually prepared under the direction of
controller, who is the manager in charge of the
accounting department
Typically, budgets are prepared annually and represent
management's plans in specific, quantitative terms
2. Directing and Motivating
Requires the ability to motivate and affectively direct
people
It includes :
Managers assigning tasks to employees,
arbitrating disputes,
answering questions,
solving on-the-spot problems,
and making many small decisions that affect
customers and employees
Managerial accounting data, such as daily sales reports
are often used in this type of day-to-day decision making
3. Controlling
Managers seek to ensure that the plan is being followed
Feedback is the key to effective control
Feedback is provided by detailed reports of various types
One of these reports, which compares budgeted to actual
results, is called a performance report
Performance report suggest :-
where operations are not proceeding as planned
and where some parts of the organization may require
additional attention.
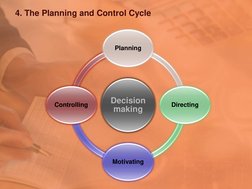
4. The Planning and Control Cycle
Decision
making
Planning
Directing
Motivating
Controlling
OBJECTIVES
Measuring Performance
Assessing Risks
Allocating Resources
Used for documenting a company's financial
transactions and keeping a record of its financial growth
Determining the total amount of assets
needed to be held by the firm
Investment in fixed or current assets
Investment in working capital
Buy or lease decision
Investing
Related to procurement of funds
Decision about debt and equity mix
Financing pattern of long, medium and
short term funds
Arranging finance for working capital
Financing
Relevant to making decisions
Types of decisions
FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING
Planning and forecasting
Financial analysis & interpretation
Communication
Facilitation of managerial control
Helpful in taking strategic decisions
Use of qualitative information
Cordination
SCOPE OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
Financial accounting
Cost accounting
Budgeting & Forecasting
Inventory control
Reporting to management
Internal audit
Tax accounting
Standard costing
Marginal costing
Decision accounting
Revaluation accounting
Break even analysis
Inter period comparison
Operations research
Statistics
Thus 3 categories of scope on the whole
1. Analysis of Financial Statements/Accounting Data Scope
This part of management accounting scope answers our
following questions
Q:- Which tools are being used for analyzing of
accounting data?
Q:- Which specific accounting data is used for analyzing
financial position, income position and solvency position?
Q:- What are main types of financial statement analysis?
Q:- What are the limitations of financial statement
analysis?
2. Interpretation Scope
After analysis through ratio analysis, fund flow analysis,
cash flow analysis or any other tool of management
accounting, our next management accounting scope is
interpretation scope. Analyzed data is also no tongue if
you have no idea how to explain it? So, this is big scope
for every wise man. Same analyzed financial statement's
meaning may be different if interpretation is given by
different account managers.
3. Decision Making Scope
"Who and how is the accounting information used for
decision making?", is the part of scope of management
accounting.
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES OF MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING
Financial management analysis
Comparative financial statements
Ratio analysis
Fund flow statements
Trend analysis
CVP analysis
Cash flow analysis
Budgetary control
Standard costing
Marginal costing
Human resource accounting
Social cost benefit analysis
Price level accounting
IMPORTANCE OF MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING
Increases efficiency
Proper planning
Measurement of performance
Maximizing profitability
Improve service to customers
Effective management control
LIMITATIONS OF MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING
Based on accounting information
Lack of knowledge
Intuitive decisions
Not an alternative to administration
Top heavy structure
Evolutionary stage
Personal biasness
Psychological resistance
PROFESSIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTANT
Most important :-
Work ethic
Analytical & problem solving skills
Listening
Spreadsheet abilities
Interpersonal skills
Understanding the business
Understanding the bottom line implications of the
management decisions
Writing
Familiarity with business process
Interpreting financial statements
Measuring & reporting revenues & expenses
Accruals, deferrals & adjusting journal entries
MANAGEMENT V/S FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
Criteria Financial accounting Management
accounting
1. On the basis of Legal
Mandating
Mandatory
Not Mandatory
2. Type of Data
Factual
Data related to buy or
make decisions, cost
decision etc.
3. Approach from users
point of view
Outside looking approach(for
external users like shareholders
and creditors)
Investigative approach
(for organizations use
only)
4. Standards for
presentation
involve accepted accounting
principles in income tax returns,
tax regulations.
No specific rules :
whatever info most
useful.
5. Time period
Usually a year, quarter or month.
Focus on completed periods
Any period year, quarter
month,week,day,even a
work-shift