Management of Open Fractures
Open Fracture
Definition
Communication of bone with the exterior
�Open Fractures
Is an emergency in orthopaedics
Associated with multiple injuries
Significant morbidity
�Open fractures:
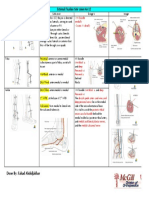
Classification
Gustilo & Anderson
Grade I
Grade II
Grade III - III A
III B
III C
�Grade I open fracture
Low velocity injury
Small puncture wound
Minimal soft tissue trauma
Prognosis is similar to a closed fracture
�Grade I open fracture
�Grade II open fracture
Moderate velocity injury
1 - 5 cm wound ( only a guide )
Moderate soft tissue injury
�Grade II open fracture
�Grade III open fracture
High velocity injury
Soft tissue damage extensive
May need secondary skin cover
�Grade III A open fracture
Large wound
Bone comminution & Contamination
Skin graft usually possible because
periosteum is often not disrupted
��Grade III B open fracture
Large wound
Bone comminution & contamination
Skin graft alone often not adequate
Local & free flaps necessary
Secondary bone procedures
�Grade III A open fracture
��Grade III C open fracture
Large wound with significant skin
disruption
Loss of bone & soft tissue
Significant bone comminution &
contamination
NEUROVASCULAR injury is present
���Grade III C open fracture
�Infection in open fractures
Grade I
less than 1%
Grade II
1-10 %
Grade III
10-50%
�Principles of management
General
Recognise an open fracture
General survey ABCs
Intravenous line & Fluids
Pain relief & analgesia
Cover the wound with moist gauze
Temporary immobilzation & splinting
�Principles of management
General
Intravenous broad spectrum antibiotic
Appropriate X-rays
Blood for GXM, FBC, U/E, CXR, ECG
Instruction for no oral intake
Arrange for emergency operation
Angiogram if indicated
Obtain informed consent for surgery
�Principles of management
Specific
General anaesthesia
Apply the torniquet (use with caution)
Irrigate the wound with saline or
chlorhexidine
Mechanical cleansing with a soft brush
Surgical preparation & draping
�Principles of management
Specific
Wound debridement - skin
subcutaneous fat
fascia
muscle & tendon
bone
blood vessels & nerves left intact
�Debridement
Remove all devitalised tissue, including
bone
Necrotic tissue increases the incidence
of complication especially infection
���Principles of management
Specific
Assess vascularity of tissue
Stabilization of the fracture
�Stabilization of the fracture
Stability is important for healing of bone
& soft tissue
External fixator commonly used
Other implants
- plates
intramedullary nails
�Principles of management
Wound coverage - never close the
wound
primarily in open
fractures
Only exception is open joint injuries
�Principles of management
Wound coverage
Dress with Tulle-grass dressing
Split skin graft rarely done on day one
��Principles of management
Re-inspect the wound at 24-48 Hrs
If necessary further debridement
Consider wound cover within the first 5
days to one week
Start interim limb physiotherapy
Observe for fracture complication
�Open fracture : Problems
General
ARDS
Atelectasis
�Open fracture : Problems
Specific
Skin necrosis
Fat embolism
Compartment syndrome
Infection
Chronic osteomyelitis
�Open fracture : Problems
Non-union
Delayed-union
Mal-union
Ischemic contractures
Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Joint contractures
����������������������Principles of management
SUMMARY
Resuscitation
Primary management
Prevent infection
Soft tissue healing
Bone healing
Rehabilitation of the limb and the patient
�Principles of management
SUMMARY
Resuscitation
Primary management
Prevent infection
Soft tissue healing
Bone healing
Rehabilitation of the limb and the patient
�Principles of management
SUMMARY
Resuscitation
Primary management
Prevent infection
Soft tissue healing
Bone healing
Rehabilitation of the limb and the patient
�Principles of management
SUMMARY
Resuscitation
Primary management
Prevent infection
Soft tissue healing
Bone healing
Rehabilitation of the limb and the patient
�Principles of management
SUMMARY
Resuscitation
Primary management
Prevent infection
Soft tissue healing
Bone healing
Rehabilitation of the limb and the patient
�Principles of management
SUMMARY
Resuscitation
Primary management
Prevent infection
Soft tissue healing
Bone healing
Rehabilitation of the limb and the patient
�������Knee