0% found this document useful (0 votes)
410 views15 pagesAddition Polymerization (Chain Growth) Step Growth Polymerization (Condensation)
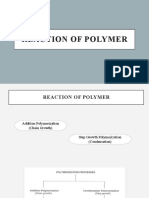
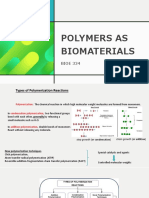
There are two main types of polymerization: step-growth (condensation) polymerization and chain-growth (addition) polymerization. Step-growth polymerization involves monomers reacting together in steps to form the polymer backbone, leading to a slow increase in molecular weight even at high conversions. Chain-growth polymerization involves monomers adding onto the active end of a growing polymer chain, allowing for rapid increase in molecular weight at early stages. Key differences between the two types include the presence of an initiator and different reaction mechanisms for chain-growth versus the same mechanism throughout for step-growth.
Uploaded by
bits_who_am_iCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
410 views15 pagesAddition Polymerization (Chain Growth) Step Growth Polymerization (Condensation)
There are two main types of polymerization: step-growth (condensation) polymerization and chain-growth (addition) polymerization. Step-growth polymerization involves monomers reacting together in steps to form the polymer backbone, leading to a slow increase in molecular weight even at high conversions. Chain-growth polymerization involves monomers adding onto the active end of a growing polymer chain, allowing for rapid increase in molecular weight at early stages. Key differences between the two types include the presence of an initiator and different reaction mechanisms for chain-growth versus the same mechanism throughout for step-growth.
Uploaded by
bits_who_am_iCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd