0% found this document useful (0 votes)
605 views18 pagesOperational Risk Management Guide
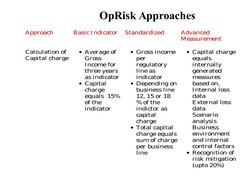
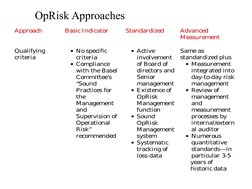
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems or external events. It includes internal fraud, external fraud, employment practices, clients, products, business disruption, system failures, and execution errors. Banks must identify, assess, monitor, control, and mitigate operational risks. There are three approaches to operational risk management - the standardized approach which uses a single risk indicator to calculate capital charges, the basic indicator approach which uses gross income to determine capital, and advanced measurement approaches which use internal models to quantify operational risk. Proper identification, assessment, measurement, monitoring, reporting, control and management processes are needed to effectively manage operational risks.
Uploaded by
SomalKantCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
605 views18 pagesOperational Risk Management Guide
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems or external events. It includes internal fraud, external fraud, employment practices, clients, products, business disruption, system failures, and execution errors. Banks must identify, assess, monitor, control, and mitigate operational risks. There are three approaches to operational risk management - the standardized approach which uses a single risk indicator to calculate capital charges, the basic indicator approach which uses gross income to determine capital, and advanced measurement approaches which use internal models to quantify operational risk. Proper identification, assessment, measurement, monitoring, reporting, control and management processes are needed to effectively manage operational risks.
Uploaded by
SomalKantCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd