0% found this document useful (0 votes)
251 views8 pagesFood Traceability Is The Ability To Track Any Food That Will Be Used For Consumption, Through All Stages of Production, Processing and Distribution
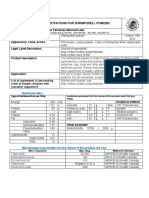
An effective food traceability system allows companies to track food through all stages of production from source to distribution. It relies on identifying suppliers, customers, and products with details like name, address, date, batch number, and quantity. This enables quick corrective actions like recalls if problems arise. Key departments responsible for traceability include procurement, logistics, quality control, and production, with batch coding used to identify goods through manufacturing and distribution.
Uploaded by
BRIGHT DZAHCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
251 views8 pagesFood Traceability Is The Ability To Track Any Food That Will Be Used For Consumption, Through All Stages of Production, Processing and Distribution
An effective food traceability system allows companies to track food through all stages of production from source to distribution. It relies on identifying suppliers, customers, and products with details like name, address, date, batch number, and quantity. This enables quick corrective actions like recalls if problems arise. Key departments responsible for traceability include procurement, logistics, quality control, and production, with batch coding used to identify goods through manufacturing and distribution.
Uploaded by
BRIGHT DZAHCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Traceability System
- Traceability in Food Processing
- Importance of Traceability
- Characteristics of a Traceability System
- Departments in the Food Chain Responsible for Traceability
- Batch Coding
- Batching of Received Goods