0% found this document useful (0 votes)
552 views12 pagesPower Distribution Analysis for LTE Networks
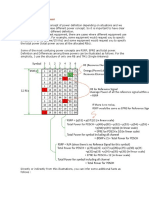
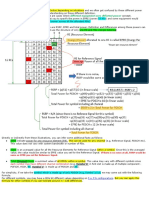
This document contains tables showing the power utilization rates, maximum power levels, total symbol power with and without rate shaping (RS), for power amplifier (PA) settings from -6 dB to 3 dB and power backoff (PB) settings from 0 to 3 across different power levels (20W, 30W, 40W) and transmission bandwidth (10 MHz). The power utilization decreases and maximum RS power increases as the PA and PB settings increase in value. The total symbol power also decreases with higher PA and PB settings.
Uploaded by
Cayo RianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
552 views12 pagesPower Distribution Analysis for LTE Networks
This document contains tables showing the power utilization rates, maximum power levels, total symbol power with and without rate shaping (RS), for power amplifier (PA) settings from -6 dB to 3 dB and power backoff (PB) settings from 0 to 3 across different power levels (20W, 30W, 40W) and transmission bandwidth (10 MHz). The power utilization decreases and maximum RS power increases as the PA and PB settings increase in value. The total symbol power also decreases with higher PA and PB settings.
Uploaded by
Cayo RianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd