0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views67 pagesIndian Banking Evolution & Structure
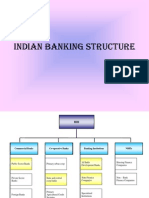
The document provides an overview of the banking system and structure in India. It discusses the evolution of Indian banks in three phases from 1786 to post-1991 reforms. It describes the types of banks in India such as public sector, private sector, foreign banks and their role in economic development through credit creation, funding priority sectors and implementing monetary policy. The functions of commercial banks like accepting deposits, lending, payment services and their contribution to the Indian economy is also summarized.
Uploaded by
Tilak RokrCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views67 pagesIndian Banking Evolution & Structure
The document provides an overview of the banking system and structure in India. It discusses the evolution of Indian banks in three phases from 1786 to post-1991 reforms. It describes the types of banks in India such as public sector, private sector, foreign banks and their role in economic development through credit creation, funding priority sectors and implementing monetary policy. The functions of commercial banks like accepting deposits, lending, payment services and their contribution to the Indian economy is also summarized.
Uploaded by
Tilak RokrCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd