100% found this document useful (1 vote)
163 views26 pagesProduction Planning Control
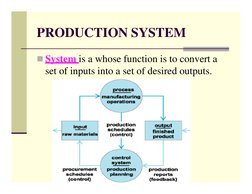
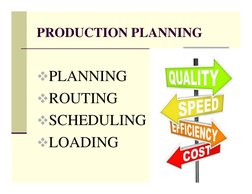
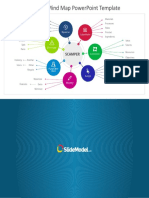
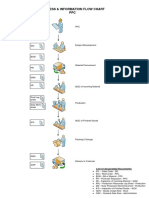
The document discusses production planning and control (PPC). It describes PPC as having three main components - production, planning, and control. Planning looks ahead to anticipate issues, while control ensures planned production is maintained. Key aspects of PPC include production planning, routing, scheduling, loading, dispatching, follow up, inspection, and corrective measures. The objective of PPC is to efficiently deliver quality products to customers on time and maximize resource utilization.
Uploaded by
Amogh KulkarniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
163 views26 pagesProduction Planning Control
The document discusses production planning and control (PPC). It describes PPC as having three main components - production, planning, and control. Planning looks ahead to anticipate issues, while control ensures planned production is maintained. Key aspects of PPC include production planning, routing, scheduling, loading, dispatching, follow up, inspection, and corrective measures. The objective of PPC is to efficiently deliver quality products to customers on time and maximize resource utilization.
Uploaded by
Amogh KulkarniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd